Parametric Study and Characterization of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Synthesized via Hydrothermal Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/mjcsm.16.1.111124Keywords:
N-CQDs, Hydrothermal Synthesis, Photoluminescence, Green Chemistry, Tauc Plots, Functional FillerAbstract
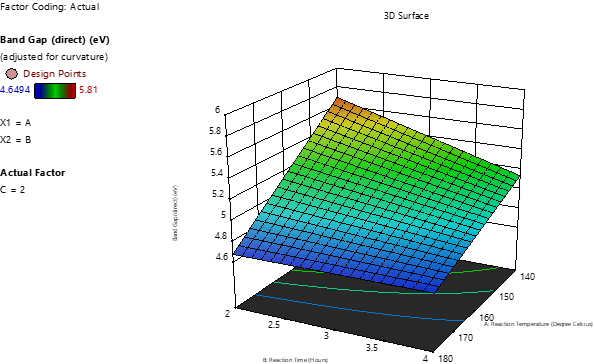
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are zero-dimensional nanomaterials known for their chemical stability, water dispersibility, low cytotoxicity, small size, biocompatibility, and photoluminescence. This study reports the synthesis of nitrogen-doped CQDs (N-CQDs) using urea and citric acid derived from calamansi lime via a simplified hydrothermal method. A 2³ full factorial Design of Experiments (DOE) optimized synthesis parameters: temperature, reaction time, and precursor ratio. Optimal conditions were 140°C, 2 hours, and a 1:1 precursor ratio. The resulting N-CQDs exhibited strong photoluminescence, excellent colloidal stability, and particle sizes ranging from 5 to 10 nm. Tauc plot analysis indicated bandgap energies up to 5.81 eV, influenced by particle size and quantum confinement. UV-Vis and FTIR spectroscopy confirmed the absorption behavior and the presence of nitrogen and oxygen functional groups, respectively, while photoluminescence measurements showed intense emission. FESEM, TEM, and EDX analyses revealed uniform spherical morphology and confirmed successful nitrogen doping. The tunable surface chemistry and optical properties of N-CQDs make them promising for bioimaging, sensing, and optoelectronics applications. The sustainable, cost-effective hydrothermal synthesis method supports scalable production for use as functional fillers in nanocomposites.
Downloads