Gigabit Passive Optical Networks: Undetected Signal Tapping
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.142.1.116Keywords:
GPON, optisystem simulator, undetectable tappingAbstract
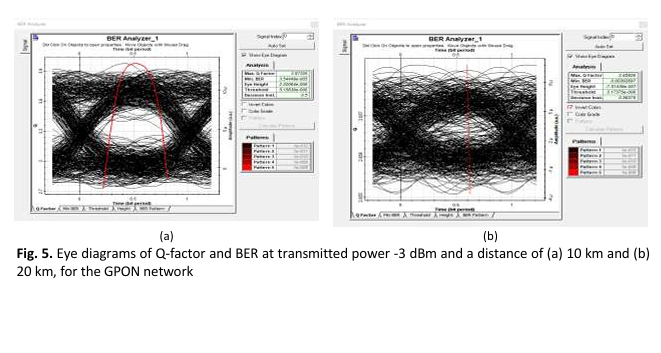
Recently, the customer high demands for increasing bandwidth and high data rates have necessitated the provision of innovative services such as video cameras and high-speed internet. Although Very High-speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technology addresses the demand for high bandwidth, it has significant drawbacks in terms of long-distance communications and high attenuation. To overcome the attenuation in cables over long distances and also to increase the bandwidth and data rate, the solution is the use of fibre optic networks. These networks are divided into passive and active networks. Among the different optical network choices, Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPONs) have acquired popularity due to their energy-efficiency because they use extremely small power to operate effectively. Furthermore, it consumes 95% less energy than copper networks and it offers a very high traffic speed of up to 100 Gbps for subscribers. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the performance of GPONs under varied transmission powers and frequencies while subjected to undetected signal tapping. The recommended approach includes eavesdropping on upstream and downstream networks without detection. This is accomplished by using an optical coupler with predetermined splitting ratios (10:90, 5:95, 2:98 and 1:99) and insertion losses (0.75 dB, 0.4 dB, 0.3 dB and 0.25 dB). Furthermore, the distance between the coupler and the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) is set to 2-10 km. To measure the quality of the intercepted signals before and after the interception, the Optisystem software is used.
Downloads