Process Optimization of Salt Recovery from Nypa fruticans Fronds using Response Surface Methodology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.142.1.108121Keywords:
Nypa fruticans, salt recovery, calcination, RSM, optimizationAbstract
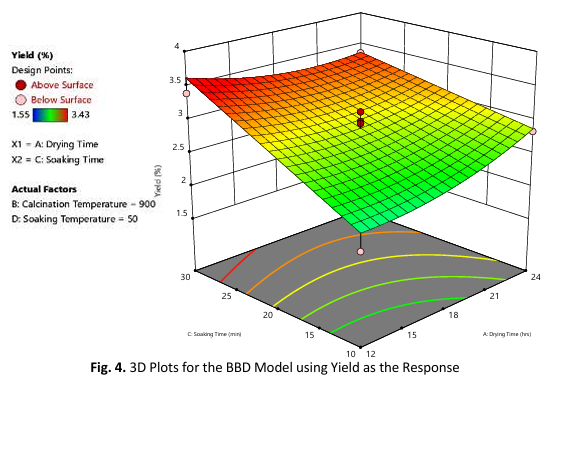
Salt, primarily sodium chloride (NaCl), has been a pivotal component of the human diet and a universal condiment since ancient times due to its ability to enhance flavor, act as a preservative, and meet physiological needs. Despite the availability of traditional unrefined salts, the production processes of nypa salt, derived from Nypa fruticans, have not been systematically investigated, and there are no standard methods for its production. This study addresses this gap by recovering salt from Nypa fruticans fronds using the calcination (ashing) method and optimizing the process conditions influencing salt recovery using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). The optimal conditions, determined to be 12 hours of drying time, a calcination temperature of 1200°C, a soaking time of 10 minutes, and a soaking temperature of 40°C, resulted in a predicted pH of 10.76 and a yield of 1.441%. These conditions were verified through additional trials, confirming model’s reliability and offering a sustainable method for salt production from Nypa fruticans fronds.
Downloads