Performance Evaluation of Cellulose Tri Acetate-Polyamide Forward Osmosis Membrane: A Mathematical Model Approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.140.1.131139Keywords:
Forward osmosis, intrinsic parameters, mathematical model, water flux, power densityAbstract
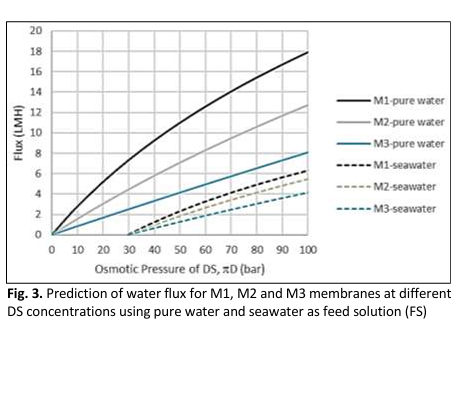
Forward Osmosis (FO) membrane is a recent membrane process used in many applications. One of the challenges in FO technology is membrane material, which suits the FO process. The selection of membrane material for FO membrane application is crucial as it determines the membrane efficiency. When characterizing the FO membrane, besides its physical and chemical properties, the intrinsic parameters; A, B, and S, which represent water permeability, solute permeability, and structural parameters, respectively, are also essential. Experiments evaluate these intrinsic parameters, which may require more work and cost. As an alternative, the mathematical model approach is beneficial in determining these intrinsic parameters. This research work applied mathematical models and was solved using Microsoft Excel to evaluate intrinsic parameters for lab-made Cellulose Tri Acetate-Polyamide (CTA-PA) membrane. Besides that, a mathematical model was also applied to predict the CTA-PA membrane performance in terms of water flux and its suitability for power generation. CTA-PA membrane with lower CTA content in the support layer exhibited higher values of A, B, and S. Lower CTA content also contributed to higher flux and higher power density as predicted by the model. The mathematical model was successfully applied in this work to determine the intrinsic parameters and predict the performance.
Downloads