Optimizing Hybrid Membrane with Kappa-Carrageenan and Silver Graphene Oxide : A Sustainable Approach using Green Solvents
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.128.1.121Keywords:
green solvent, dimethyl sulfoxide, silver-graphene oxide, hybrid membraneAbstract
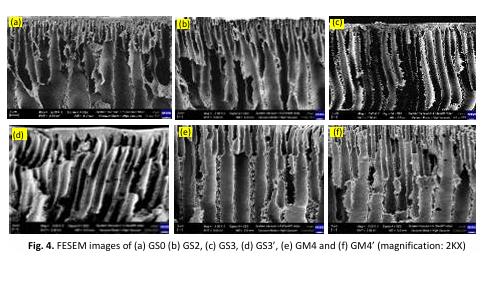
The application of toxic solvents in membrane production poses significant risks to human health, environmental sustainability, workplace safety, and regulatory compliance. In response to the increasing demand for sustainable practices, recent research had shifted towards developing greener alternatives to achieve more sustainable membrane principle. Solvents such as ethylene carbonate (EC), dimethylacetamide (DMAc), and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) have demonstrated potential due to their minimal environmental impact and effectiveness in maintaining the membrane performance. This study explores the fabrication of hybrid membranes polysulfone (PSf) with kappa-carrageenan (k-car) embedded with silver graphene oxide (Ag-GO) using less toxic solvents. The additives, k-car, serve as a pore-forming agent to enhance hydrophilicity, while Ag-GO NPs as an antibacterial agent and reduce the hydrophobicity of PSf. The membranes were fabricated by the wet phase inversion technique, with embedment of k-car and Ag-GO into a mixed-matrix of PSf casting solution. The inclusion of k-car and Ag-GO NPs significantly enhanced the hydrophilicity from 68.52 to 57.32 degree and porosity from 63 to 88%, respectively. Membrane performance analysis demonstrated that all membranes, except GS2, achieved Fe2+ and Mn2+ removal rates above 95%. Notably, the GS3 membrane exhibited the highest water flux at 213.12 L.m-2 h-1 and the highest iron and manganese removal rates, at 98.1 and 99.8%, respectively. The GS3 membrane demonstrates exceptional performance due to its optimized porosity, increased hydrophilicity, high permeate flux, and enhanced ionic solute removal efficiency. This performance is further intensified by using DMSO as a green solvent during fabrication which improves membrane structure and function while aligning with sustainable processing standards. This study underscores the potential of green solvents in producing high-performance, environmentally friendly membranes for water treatment applications.
Downloads