Application of Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network for Transformer Health Index Monitoring
Keywords:
dissolve gas analysis, key gas method, multilayer perceptronAbstract
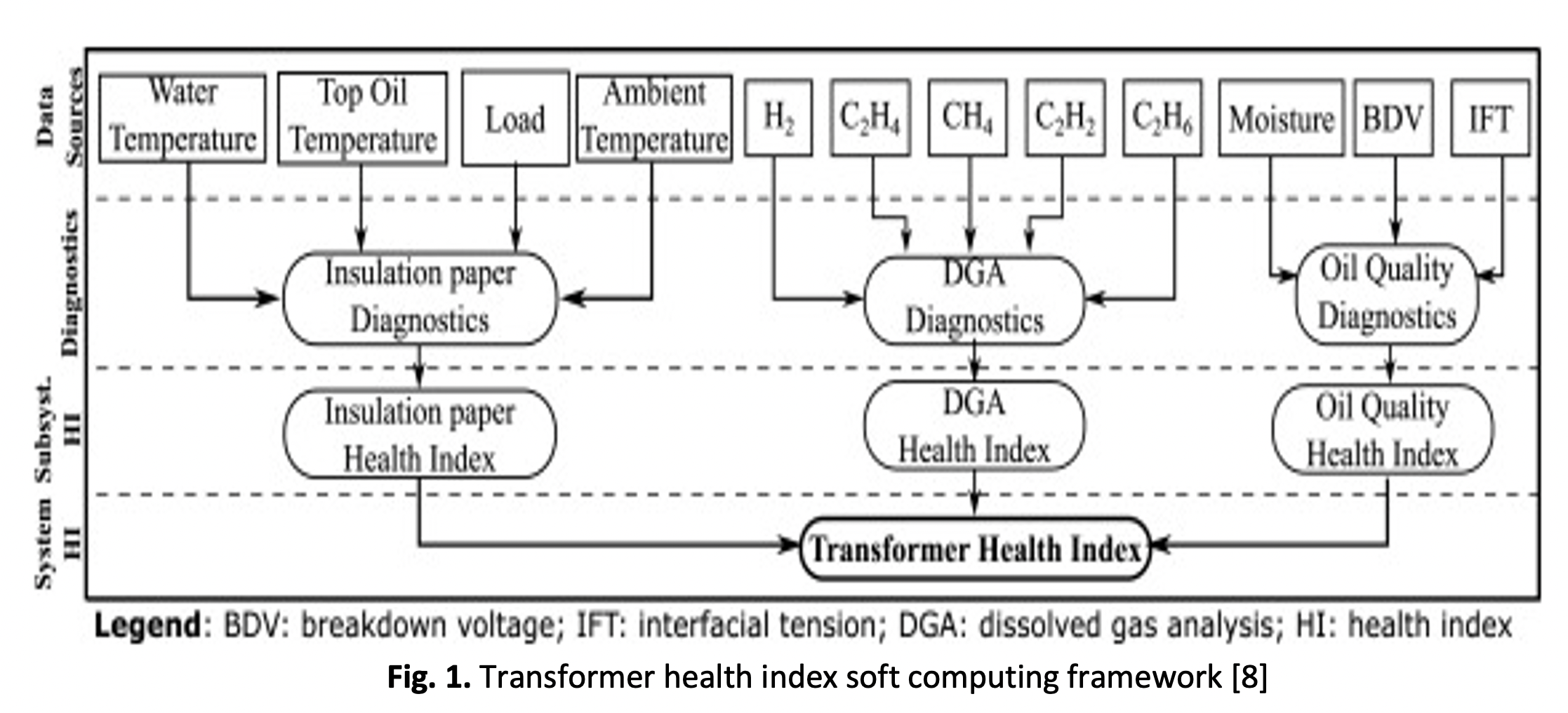
Dissolve Gas Analysis (DGA) is a method of diagnosis employed in the assessment of transformers, enabling the distinction between transformers in optimal operating condition and those requiring scheduled repair. The primary objective of DGA is to accurately identify and characterise the issues arising from different gas forms within transformers. The Key Gas Method (KGM) analysis is a commonly employed approach within the field of DGA. The KGM method is employed for predicting the health index of transformers by analysing the production of gases within the transformer. The study involved the arrangement of many classifiers to achieve optimal performance, taking into consideration four specific configuration parameters. The multilayer perceptron (MLP) network, K-Nearest Neighbourhood (KNN), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), and Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithms are used to classify the data. The accuracy of the MLP network surpasses that of other classifiers, achieving a rate of 90.67%. Additionally, the mean squared error (MSE) for the MLP network is 0.92. Three distinct training algorithms were chosen for the purpose of training a MLP using the Backpropagation (BP), Lavenberg Marquardt (LM), and Bayesian Regularisation (BR) training procedures. At the conclusion of the simulation, the BR training algorithm demonstrates superior performance, achieving an accuracy rate of 91.25% and a MSE value of 0.93.
Downloads