Compressive Strength and Density in Fresh and Dried Cube Analysis of Autoclaved Aerated Concrete in Cooperating Glass Industrial Waste
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.136.1.92107Keywords:
autoclaved aerated concrete, gypsum, compressive strength, density, glass waste, replacementAbstract
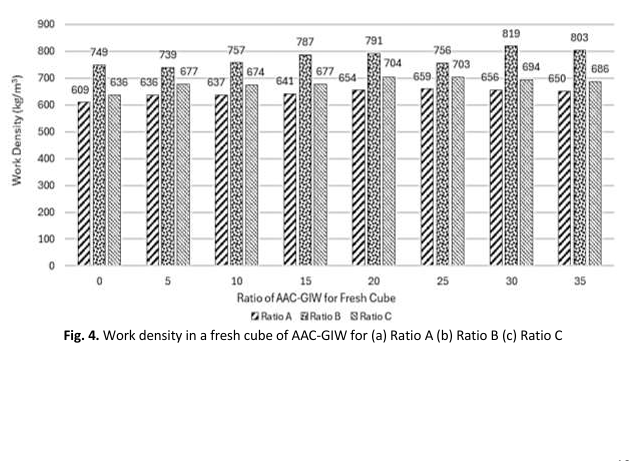
In the pursuit of sustainable construction materials, cooperating industrial waste into innovative building solutions has emerged as a promising way. Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC) stands out as one such eco-friendly material renowned for its lightweight and insulating properties. The research highlighted that glass Industrial waste (GIW) had the potential to improve the strength and fire resistance of AAC due to its excellent properties of GIW in terms of physical, mechanical and thermal performances. The possibility of GIW was explored by including it in AAC concrete and analysing the effect of varying additions on the properties of AAC. This fundamental research proposed different percentages of GIW composition (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and 35%) as a partial replacement for 70% (Sand+ Gypsum) mixed with different amounts (0.1% and 0.065%) of Aluminium paste. Then, the same percentages of the GIW composition (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and 35%) were used as a partial replacement to reduce the silica content of 68% (Sand+ Gypsum) mixed with 0.1% Aluminium paste. All specimens underwent a steam curing process for 12 hours at a temperature of 180°C and a steam pressure of 13 bars in an autoclave machine to produce Autoclaved Aerated Concrete based on Glass Industrial Waste (AAC-GIW). These aspects were crucial in determining the optimum composition of glass waste that could influence the physical, mechanical and thermal properties of AAC-GIW. The optimum composition of GIW, sand, gypsum, lime, cement and aluminium paste as an expanding agent in AAC-GIW were the factors contributing to high strength. The compressive results were analysed in 3 different ratios (Ratio A, Ratio B and Ratio C) for fresh cubes and dried cubes, the work density and dry density. It is revealed that 15% GIW for ratio C is an optimum compressive strength at 2.43 MPa work density of 677 kg/m3 for fresh cubes as a sand replacement, in dried cube condition, 15% produces the highest compressive strength at 6.64 MPa of 661 kg/m3 for Ratio B. At different ratios, the most effective GIW content differed, emphasizing the requirement for modifications in AAC-GIW formulations specific to the AAC.
Downloads