Examining the Impact of Negative Bias Temperature Instability on the Performance of Domino Logic Circuits
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.136.1.154166Keywords:
negative bias instability (NBTI), domino logic circuit, interface trap (Nit), oxide trap (Not), delayAbstract
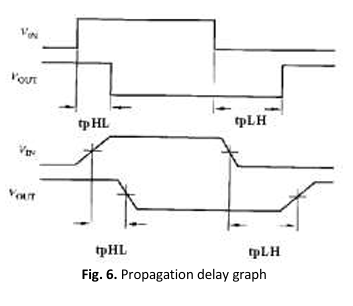
Negative Bias Temperature Instability (NBTI) poses a notable reliability concern in Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs), causing an aging effect that alters threshold voltage and reduces drain current. This effect holds particular significance in sub-micrometre CMOS circuitry. This study focuses on assessing NBTI's impact on domino logic circuits, exploring various NBTI defect mechanisms like interface trap (Nit) and oxide trap (Not). Evaluations extend to NOR and NAND domino logic circuits, analysing delay and average power to gauge NBTI effects. The study employs the Predictive Technology Model (PTM) based on 32nm technology, coupled with the MOSRA model, to illustrate circuit dependability. Simulations involve varied stress temperatures, revealing a proportional degradation in delay with increasing temperature. Specifically, when Nit serves as the sole defect mechanism, the time exponent stands at 0.25, whereas Nit and Not together reduce this exponent to 0.167. Higher stress temperatures correlate with increased delay, reduced average power, and a shift in threshold voltage towards higher values over prolonged stress durations.
Downloads