Impact of Attachment Styles on Social Isolation and Impulsiveness among Patients with Gender Dysphoria
Keywords:
Relationship attachment, social isolation, impulsivenessAbstract
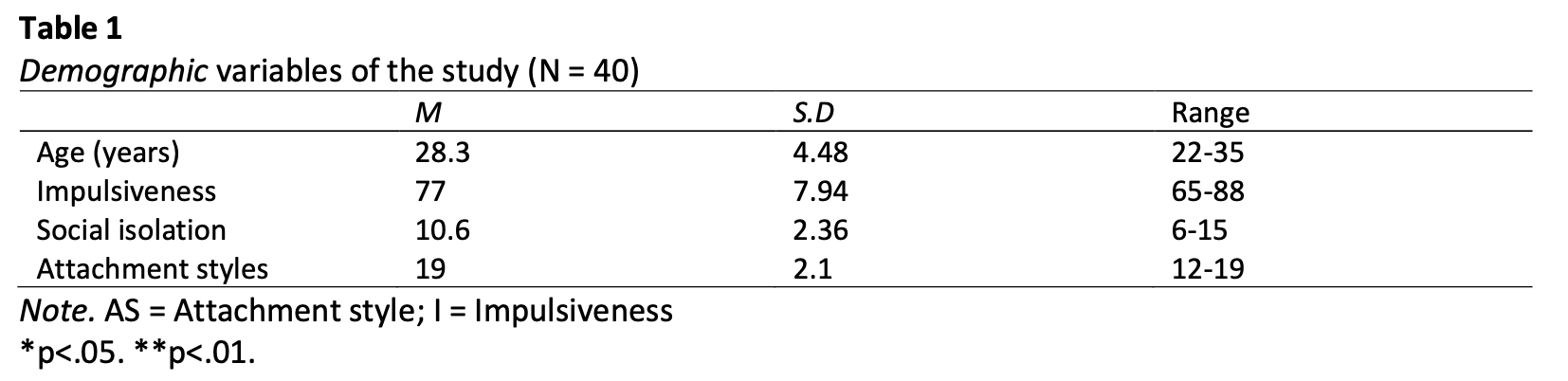
Present study examined links between social isolation, impulsiveness and relationship attachment in patients with gender dysphoria. Total number of patients was (N = 40) with age range of 25-40 years (M = 28.3; SD = 4.48). Sample was selected through purposive sampling method. To measure adult attachment styles, impulsiveness and social isolation, relationship questionnaire (RQ), impulsiveness scale(revised) and friendship scale was used respectively. Statistical analysis revealed that patients with gender dysphoria manifested higher levels of social isolation and impulsiveness. While, Pearson correlation analysis indicated significant negative correlation between impulsiveness and social isolation. Moreover, results of linear regression analysis identified all attachment styles as significant predictors of social isolation. In addition, secure attachment style is significant negative predictor of attention impulsiveness and non-planning impulsiveness. Furthermore, the pre-occupied attachment style positively predicts the non planning impulsiveness and attention impulsiveness. Similarly, dismissing attachment style negatively predicts non-planning impulsiveness. Findings of the study can provide a significant aid for mental health practitioners working with gender dysphorics. It can also help in developing a better management plan as it gives more insight in understanding different aspects of their psychological life.