Green Engineering with Nanofluids: Elevating Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.16.1.1934Keywords:
Nanofluid, heat transfer, renewable energyAbstract
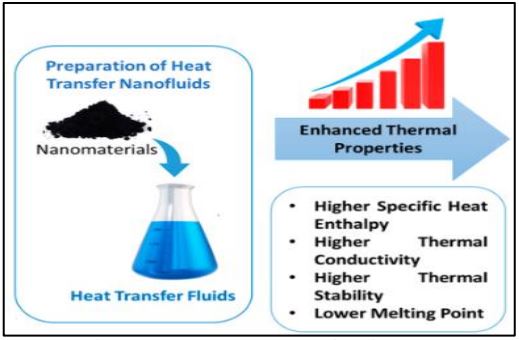
Colloidal suspensions of nanoparticles in a base fluid, known as nanofluids, have gained attention as a promising green technology with a lot of promise to address issues with sustainability and energy efficiency in a variety of industries. The main features and uses of nanofluids as a sustainable solution are summarized in this paper. Due to their high thermal conductivity and high surface area to volume ratio, nanoparticles give off exceptional thermal and heat transmission capabilities. They are a desirable option for boosting the effectiveness of heat exchange systems, such as refrigeration, air conditioning, and cooling in electronic equipment, due to their improved qualities. Higher heat transfer rates and lower energy consumption can be achieved by using nanofluids as coolants or heat transfer fluids, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions and energy expenditures. Nanofluids have also found use in the realm of renewable energy, where they can improve the performance of geothermal and solar thermal collectors. The capture and conversion of renewable energy sources can be greatly enhanced by using nanofluids as working fluids in these systems, helping to create a greener and more sustainable energy landscape. Additionally, environmental cleanup and pollution management could benefit from the use of nanofluids. They are appropriate for uses including wastewater treatment, oil spill cleanup, and air purification because of their special features that allow for effective heat transfer and pollutant absorption. Furthermore, nanofluids can significantly contribute to lowering the amount of water and energy used in industrial operations, thus advancing sustainability objectives. The numerous uses of nanofluids as a green technology are highlighted in this paper, with an emphasis on their potential to improve energy efficiency, lessen environmental impact, and contribute to a more sustainable future. As this area of study and development develops, nanofluids will be in a position to play a crucial part in resolving the urgent problems of our day.