Influence of Molybdenum Disulphide (MoS2) Nanoparticles Loading in Treated Used Palm Oil Bio-lubricant on Surface Roughness during Turning of AISI420
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.14.1.17Keywords:
Bio-lubricant, Zinc Dialkyldithiophosphate, MoS2 nanoparticles, AISI420 cuttingAbstract
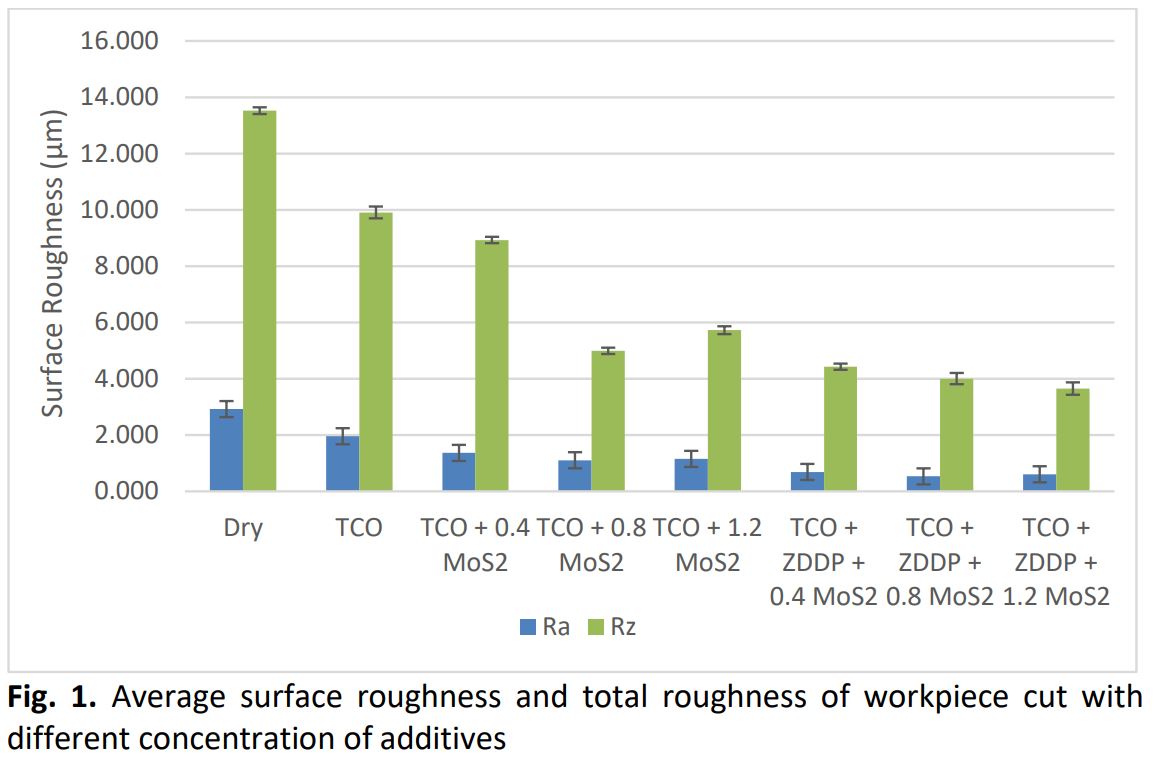
The environmental impact and non-biodegradability of petroleum-based lubricants has caused some researchers to shift the formulation of lubricant formulation using plant-based oil, However, food security has caused concerns in development of new bio-lubricants. In this study, treated used cooking palm oil added with Zinc Dialkyldithiophosphate and Molybdenum Disulphide nanoparticles were used as lubricant to assist the cutting of hardened martensitic stainless steel AISI420 using coated carbide tool. Surface roughness of the cut workpiece was investigated using a surface roughness tester. From the study, treated used cooking oil added with ZDDP and 0.8wt% MoS2 nanoparticles displayed the lowest average surface roughness of workpiece with Ra = 0.532µm and total roughness Rz = 4.006µm. This concluded that the new formulated bio-lubricant can successfully replace the readily available commercial cutting fluid as it produces a low surface roughness during cutting process.