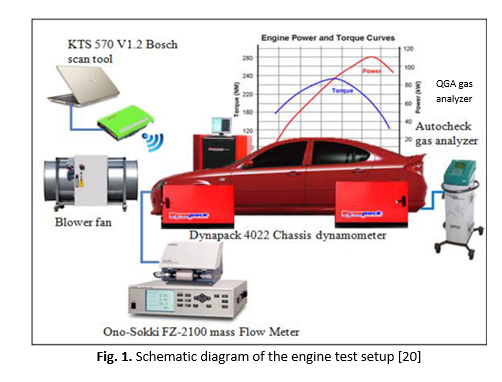
Effects of Oxyhydrogen (HHO) Gas Supplementation on Performance and Emissions of a 1.6L Spark Ignition (SI) Engine at Various Load Conditions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arefmht.21.1.149164Keywords:
Oxyhydrogen gas, HHO supplementation, spark ignition engine, engine performances, exhaust emissionsAbstract
This study investigates the effects of Oxyhydrogen (HHO) gas supplementation on the performance and emission characteristics of a 1.6L, 4-cylinder Multi-port Fuel Injection (MPI) spark ignition engine under varying load conditions. A dry-cell HHO generator utilizing potassium hydroxide (KOH) electrolyte at different molarities (0.3M, 0.5M, 0.7M, and 1.0M) was employed, with the generated gas supplied directly to the intake manifold just before the throttle body. The engine was tested in stock condition using only RON95 gasoline, while HHO testing was conducted in a dual-fuel configuration, combining RON95 gasoline with HHO gas. Performance and emissions were evaluated across engine speeds from 1500 to 3000 rpm at throttle valve positions of 25%, 50% and 75%. Brake power and torque were enhanced by up to 3.67% and 3.40%, respectively, with the most notable improvements occurring at 3000 rpm of engine speed. Brake-specific fuel consumption was reduced by up to 1.94%, although the highest molarity (1.0M) occasionally led to efficiency penalties. Emission measurements indicated significant reductions in CO and HC emissions, up to 11.90% and 22.98%, respectively, while monitoring CO2, NOX, O2, and lambda/air-fuel ratio (AFR). The most favorable HHO concentration range was identified as 0.5–0.7M. These findings demonstrate that controlled HHO supplementation can effectively enhance fuel economy and emission performance in SI engines without major mechanical modifications, contributing to the advancement of more environmentally sustainable internal combustion technologies.
Downloads