Machinability Assessment of Hole-Making in Rubberwood–Plastic Composites Using Abrasive Waterjet Cutting
Keywords:
Wood plastic composites, Hole-Machining, Abrasive waterjet cutting, Drill bitAbstract
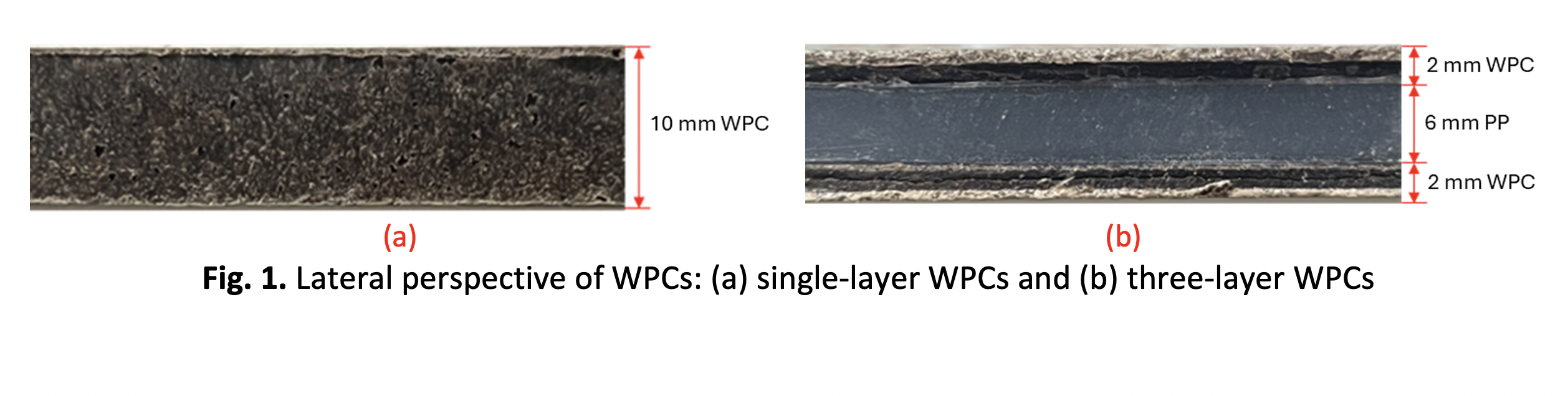
The application of wood-plastic composites (WPCs) in industrial and structural applications has increased; however, the secondary machining process of hole-making for assembly remains challenging due to tool wear, dimensional inaccuracy, and surface defects in conventional drilling. Therefore, this study examines the machinability of abrasive waterjet (AWJ) cutting as an alternative approach for creating holes in single-layer and three-layer WPCs. Experiments were conducted using different cutting parameters, including water pressure, traverse speed, abrasive mass flow rate, and hole diameter. The effect on hole characteristics, roundness, and surface quality was analyzed. The results indicated that AWJ achieved through-cuts in both single-layer and three-layer WPCs, providing greater hole roundness and surface polish, while WJ produced complete cuts mainly at 350 MPa. The recommended AWJ parameters are abrasive flow rate of 6.67 g/s, water pressure of 350 MPa, and traverse speed of 30 mm/s, results in a roundness of 0.351 mm. A regression model was created to predict roundness, attaining an acceptability of 84.8%. A comparison with drilling bit suggested that AWJ cutting enabled shorter processing times, more flexibility, and without tool changes, although yielding lower roundness values. The results indicate that AWJ is a feasible and efficient alternative for hole fabrication in WPCs for manufacturing purposes.Downloads