Energy Management and Operational Optimization of Data Centers in a Smart Grid with Wind Power Integration and Service Delay Constraints
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.138.1.162174Keywords:
Energy Management, Operational Optimization, Wind Power Integration, Service Delay Constraints, Smart GridAbstract
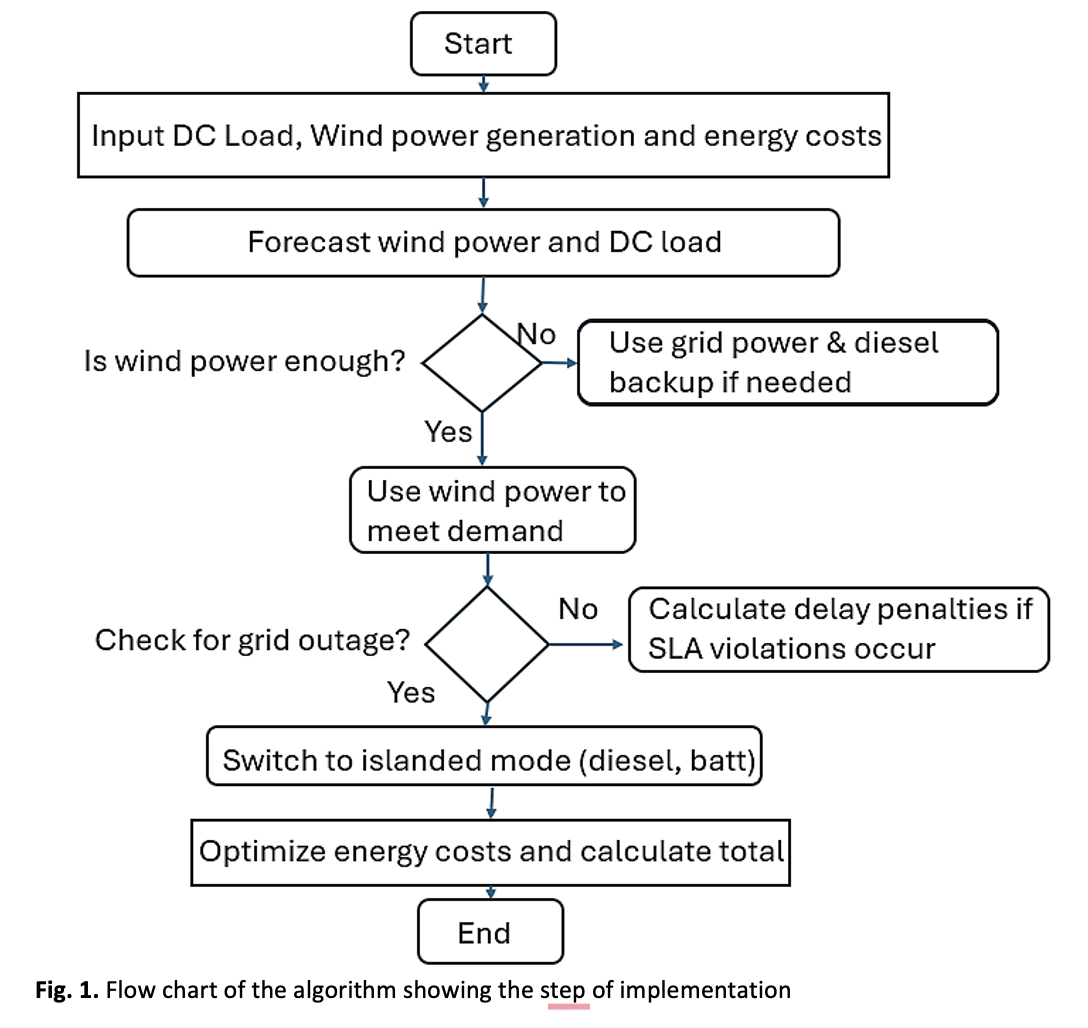
The paper will present a framework for management in energy and operational optimization of smart grid integrated data centers (DCs) under the operation of wind power generation, with diesel generators as a backup source. The generated wind power is not reliable due to its desirable intermittent nature, and it will require energy to be drawn from the grid so that the DC could operate without interruption. This paper considers the nature of mix to be supplied, where the total maximum peak loading of 35% of the total consumption of the DC may be made out of the wind and when in normal operation while in grid outage it is required to work in an islanded mode and it would use diesel to generate power for the fulfillment of this demand. The paper provides an elaborate analysis of DC workload and service delay including penalties for delay under Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) Service Level Agreements (SLA). It further relates to power consumption modeling that incorporates server utilization and Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE), which indicates variations in power consumptions during the day concerning workload demands. This work proposes strategies to balance the trade-offs between energy costs, service reliability, and delay penalties to optimize DC operations in both grid-connected and islanded modes.Downloads