Diagnosis of Skin Melanoma Utilizing an Advanced Combination of Improved Meta-GVF Algorithms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.140.1.8395Keywords:
Melanoma, early detection, machine learning, diagnostic systems, meta-GVF algorithmsAbstract
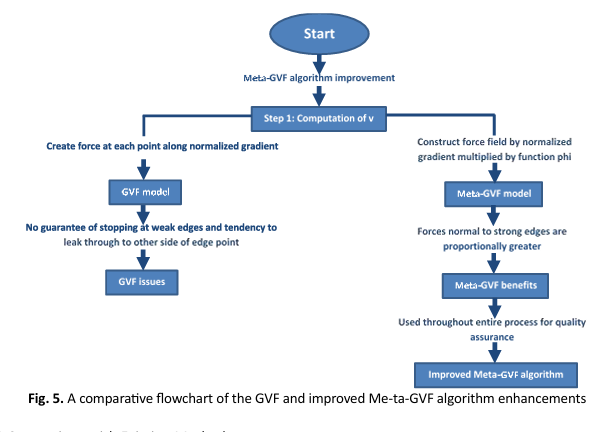
The rising global prevalence of skin cancer has become a significant public health concern. Although melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancer cases, it is responsible for the majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Early detection is critical, as it can raise the five-year survival rate to over 90%. However, the prognosis for metastatic melanoma remains poor, with a five-year survival rate of only 10–15%. Computer-aided diagnostic systems, utilizing machine learning and deep learning models, have shown promising results in analyzing skin lesions and detecting melanoma. Despite these advancements, diagnostic accuracy is still limited by challenges such as the lack of distinct color variation in skin lesions and the absence of reliable methods for assessing melanoma thickness—a crucial factor for prognosis and treatment planning. This study introduces an innovative approach to diagnosing skin melanoma using an advanced Meta-GVF algorithm, achieving an accuracy of 85.5%. The main finding is that, through shape modeling and well-chosen initial conditions, the contour can effectively move toward the correct boundary. Additionally, with further development, boundary detection techniques could help automate the initialization process in Meta-GVF, enabling the automated diagnosis of skin abnormalities.
Downloads