Design and Control of Self-Balancing Electric Motorcycle with Simulink Auto-Tune Pid Controller
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.141.1.113Keywords:
Inverted pendulum, PID controller, self-balancing vehicleAbstract
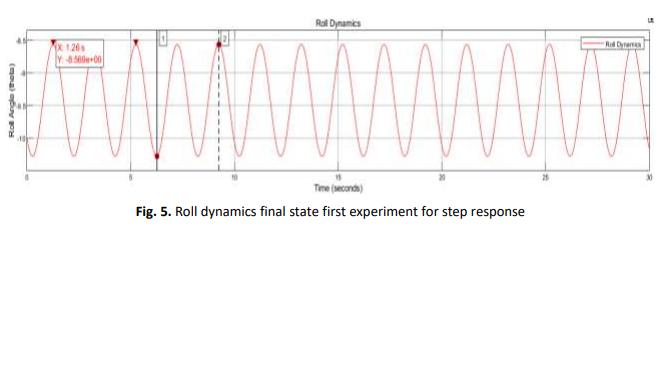
This project describes the design and control of a self-balancing electric motorcycle with a Simulink PID controller. In this system, self-balancing refers to the ability to balance by itself without any assistance from external forces. The self-balancing electric motorcycle should also be able to bounce back after being given external force. This project draws on the theoretical principles of the inverted pendulum. The inverted pendulum system, unlike many other control systems, is inherently unstable. Due to this condition, a controller has to be designed so that the system reaches stability in the unstable state. This project presents motorcycle modeling, designing, and implementing a controller using a PID controller. PID controllers are implemented to minimize error to the least possible value and improve the performance of the controller. The ability to successfully perform self-balancing electric motorcycle is greatly reliant on the proportional gain, (), integral gain (), and derivative gain () values utilized to control the rotation around the front-to-back axis called roll angle and rotation around the vertical axis is called yaw angle. The objective of this research project is to stabilize the motorcycle at speeds less than 10 km/h. The result of the model is compared and analyzed within various , , and values. The response of the system depends on the values of setting time and overshoot percentage. The simulation results show that the controller cannot balance the robot.
Downloads