Enhanced Model Compression for Lipreading Recognition based on Knowledge Distillation Algorithm
Keywords:
Lipreading, Deep learning, Model compression, Knowledge distillationAbstract
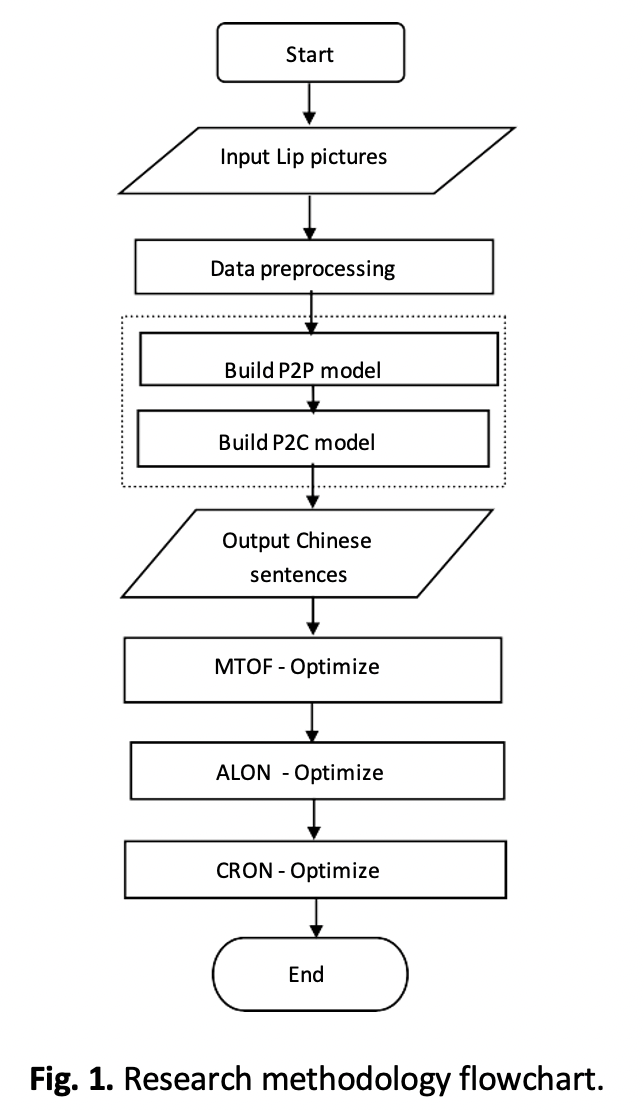
Lipreading is understanding what a speaker is saying by observing changes in the speaker's mouth. The lipreading recognition model LipPC-Net proposed in this paper is built with a large Chinese lipreading data set based on Chinese phonetic rules and grammatical features and consists of two main parts: the P2P sub-model and the P2C sub-model. The P2P sub-model is a model for identifying pinyin sequences from pictures, while the P2C sub-model is a model for identifying Chinese character sequences from pinyin. However, Chinese language features are rich and fuzzy, and the training optimization of lip-reading model requires high GPU computation and storage, so it is difficult to realize large-scale application. Therefore, three knowledge distillation compression algorithms are proposed in this paper: Three different knowledge distillation compression algorithms, an offline model compression algorithm based on multi-feature transfer (MTOF), an online model compression algorithm based on adversarial learning (ALON), and an online model compression algorithm based on consistent regularization(CRON) to complete the compression of the Chinese character sequence output by the model. Three compression algorithms are used to fit and learn the transformation between different features, so that portable mobile terminals with limited hardware resources can carry the model. Thus, it can realize the practical application value of assisting the communication of deaf-mutes.
Downloads