Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Models for Emotion Recognition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.135.1.5376Keywords:
machine learning algorithms, autism, emotion recognition, EEG signals, Random ForestAbstract
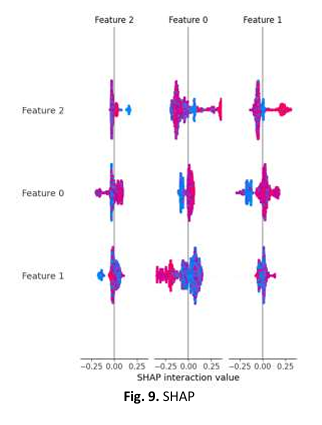
Emotion recognition is a part of artificial intelligence that detects human emotions using machine learning (ML) techniques, thus analysing inputs like facial expressions, voice tone and physiological signals. Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) experience difficulties in social interaction and communication and exhibit repetitive behaviours. ML has greatly helped autistic people by analysing their behavioural data to detect and comprehend slight emotional indicators. This paper explores the abilities of ML-based systems to recognize and understand these emotional cues, which are of great importance for improving communication and intervention methods. We employed datasets of EEG signals and applied principal component analysis (PCA) and uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) for dimension reduction. We used ML models such as Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machines (SVM), Logistic Regression, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and 1D Convolutional Neural Network (1D-CNN) on the datasets. The evaluation of the models relied on metrics like accuracy, precision, recall and F1-score to determine their ability to recognize emotions in EEG signals. The RF model achieved 95% accuracy on the original dataset and maintained robustness with PCA (88%) and UMAP (85%), outperforming other models in classification accuracy and stability. Future research should concentrate on broadening the datasets to include a more varied group of participants and combining multimodal data, using advanced deep learning methods to increase the accuracy and the feasibility of emotion recognition systems for personalized ASD therapies.
Downloads