Enhanced Cybersecurity Efficiency and Android Malware Classification towards Carbon Emission Reduction: Two Phase Ensemble Approach
Keywords:
android malware classification, ensemble, Genetic Algorithm, Machine Learning, SDGAbstract
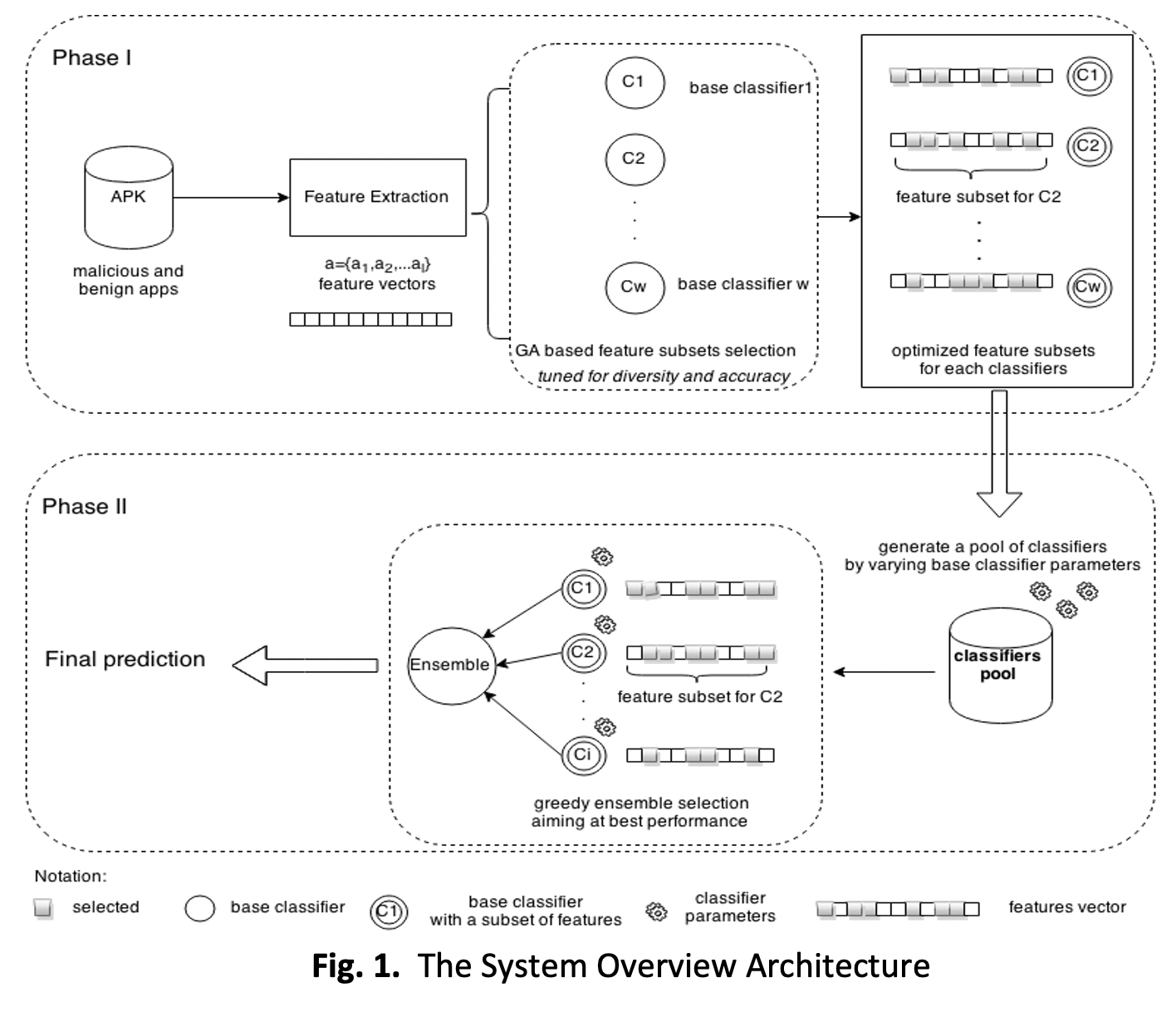
The environmental impact of cybersecurity, especially on the agenda of energy consumption and carbon emissions, becoming one of the concern in cybersecurity industry. Automatic Android classification plays a vital role in combating the rapidly growing number of Android malware variants. In this paper, a highly accurate ensemble classification approach for detecting malicious Android apps is described. In the design of this two-phase ensemble, diversity is considered as one of the main aspects to be taken into account. In the first phase, a large number of discriminative features for classification are extracted from Android application package (APK) files, and a Genetic Algorithm(GA) based feature subset selection procedure is applied on different types of base classifiers. In the second phase, an initial pool of classifiers is constructed by varying parameters of base classifiers, and a heuristic search process is conducted aiming at pruning the learning models in the initial pool. The results shown that evaluation with 1554 malware apps and 2400 free popular apps reported a detection accuracy of 97.6% and ROC curve (AUC) value of 99.5% that is better than the existing static analysis based method. The integration of these technologies into malware detection processes not only bolsters security but also supports environmental sustainability in information technology (IT) practices. These action would drive the green IT towards sustainable development goals (SDG).
Downloads