Distribution Network Expansion Planning and Integration of Distributed Energy Resources Considering Massive Penetration of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations in Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.130.1.112124Keywords:
Distributed energy resources, distribution networks, electric vehicle charging station, expansion planningAbstract
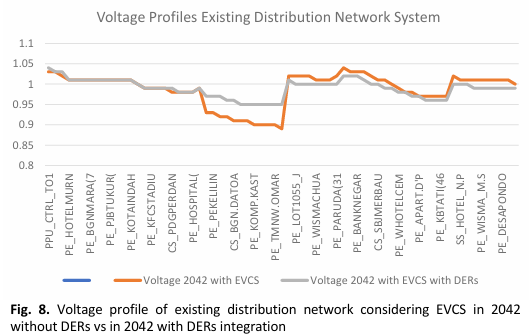
By 2030, Malaysia's Low Carbon Mobility Blueprint 2021-2030 anticipates 20,000 Electric Vehicles (EV) in the market. The increase of EV population as transportation due to the environment issue has caused sudden impact to the distribution network system which needs to be tackled urgently. The massive penetration of EVCS into the distribution network system, especially at houses, parking lot and any strategic places either for slow, medium or fast charging, will lead to other crucial issues such as increment of power losses and voltage violations. Hence, Distribution Network Expansion Planning (DNEP) strategies become critical to adhere this issue. Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) with low-carbon efforts are one of the potential sources of power to overcome this issue that have a substantial influence on system reliability and security, particularly in power losses and voltage profiles characteristics. This research paper presents optimal techniques for development of DNEP with integration of DERs towards achieving multi-objectives of minimizing power losses and improving the voltage profiles. These techniques are based on industry-based technical analysis conducted using the Power System Simulator/Advanced Distribution Engineering Productivity Tool (PSS/ADEPT) software. The proposed methods are tested on the realistic 11kV 69-bus radial distribution network. The simulation results successfully demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method for DNEP to minimize power losses and voltage profile improvement in the distribution network system due to the massive penetration of EVCS along the 20 years of DNEP horizon in Malaysia.
Downloads