Investigating the Determinants of Cloud Computing-Software as a Service Adoption in Pakistani SMEs from the Perspective of SME Managers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.127.1.3248Keywords:
cloud computing, software as a service, TOE, OST, SMEsAbstract
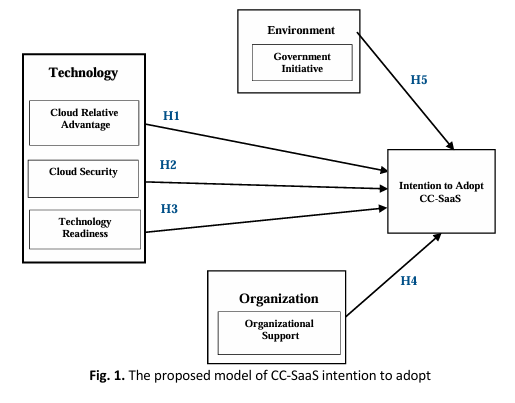
Pakistan's small and medium enterprises (SMEs) sector oppose many challenges, encompassing resource mismanagement, infrastructural deficiencies, a burgeoning volume of data and impediments hindering organizational growth. These challenges include financial constraints from corruption and insecurity and limited IT resources and infrastructure access. Consequently, adopting Cloud Computing Software as a Service (CC-SaaS) presents a potentially advantageous solution. It offers SMEs an avenue to enhance operational efficiency through cost-effective technological integration, facilitating improved e-services for citizens and promoting knowledge sharing for increased benefits. However, the adoption of CC-SaaS remains relatively limited within the Pakistani SME landscape, beset by numerous obstacles, like data privacy, legal compliance and security concerns. Despite the extensive literature on factors influencing cloud computing (CC) adoption, most of these studies emanate from developed nations. More attention has been devoted to examining the adoption of CC-SaaS. Indeed, within countries marred by conflict and instability, the adoption landscape of CC-SaaS remains largely uncharted. This study addresses this knowledge gap by investigating the determinants influencing organizational intentions regarding adopting CC-SaaS among Pakistani SMEs operating in an environment fraught with conflict. It necessitates examining how the prevailing conflict dynamics in Pakistan might impact CC-SaaS adoption within the country. Ultimately, this research aspires to benefit SME organizations in Pakistan and contribute to validating measurement frameworks for future studies. The study's conceptual model draws upon the Technology-Organization-Environment theory and the Organization Support Theory. Expert opinions informed the identification of moderating effects. Data was collected from a sample of 368 SME managers operating in Pakistan. Subsequently, the collected data underwent analysis employing the Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) approach. The study findings indicate that the impacts of technology organization, environment and Organization Support Theory on CC-SaaS adoption are statistically significant.
Downloads