Designing 3D Printed Electromagnetic Wave Absorber
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.130.1.8092Keywords:
Silica, electromagnetic absorber, low cost, higher frequencyAbstract
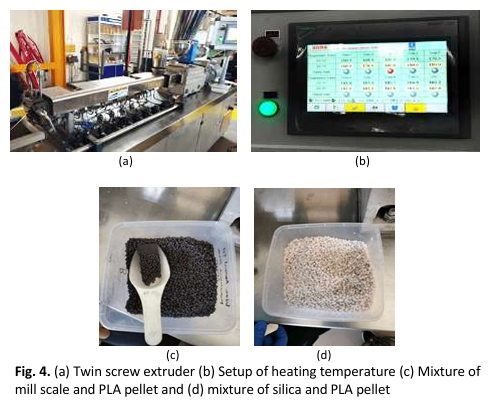
Recent years, electromagnetic (EM) wave radiation has been regarded as an alarming danger for commercial appliances, biological systems, and high-quality information technology. The fabrication of EM wave absorbers is a crucial technological advancement in the field of EM wave management that can absorb the EM wave interference. Various materials that were developed to absorb EM wave interference are high cost, environmental impact, and are harmful to human health and other equipment. Therefore, this research introduces single and multilayer absorber that were fabricated by using the filler materials based on silica from beach sand and mill scale from industrial waste. The prepared polymer composite samples were also 3D printed with the desired shape and size so that it met the requirement of using it for any applications. The single layer and multilayer polymer composite thickness were fixed at 1 mm and 2 mm respectively. The microstructural phase formation, morphological study, particle size analysis and elemental analysis were analyzed by using X-ray diffractometer (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) respectively. The microwave characterization of the polymer composite samples was analyzed by using Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) at 4 to 8 GHz frequency range. The results shows that single layer and multilayer have triple resonance peaks and may absorb the electromagnetic wave with the minimum reflection loss peak in between 5.5 to 6.5 GHz. It shows that the sustainability factor and low cost of silica-based sand and industrial waste-mill scale makes it highly attractive as a potential filler material that can be used as an EM wave absorber in many applications.
Downloads