Performance Evaluation of Vapor Compression Refrigeration System Using Different Types of Condensers Cooling Medium
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.125.1.6878Keywords:
VCRS, nanofluid, multi condenser, performance improvement, Titanium dioxide (TiO2)Abstract
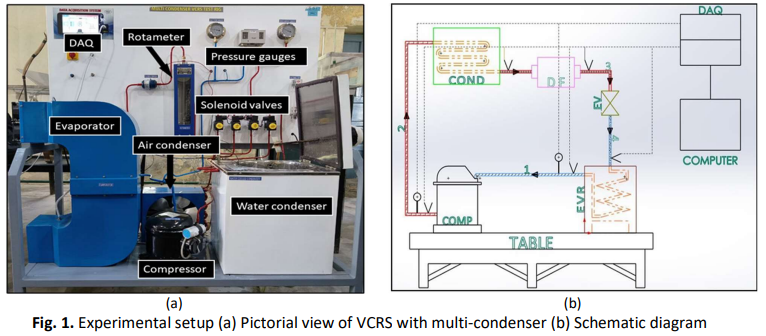
This research investigates the performance of a vapor compression refrigeration system (VCRS) using different condenser cooling mediums: air, water, and nanofluid containing 0.02% (v/v) titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in water as base fluid. The primary objective is to comprehensively evaluate and compare the performance of these condenser types within the VCRS, aiming to identify the most efficient and eco-friendly condenser cooling medium. The research also explored different mass flow rates of air velocity in the evaporator, ranging from 0.7 to 2.7 m/s. The experimental results reveal that nanofluid-cooled condensers outperform water-cooled and air-cooled condensers in terms of coefficient of performance and cooling effect. This is due to the higher thermal conductivity of nanofluids, which results in a higher heat rejection rate in the condenser. The choice of cooling medium for the condenser depends on various factors such as cost, maintenance requirements, and operating conditions. This research reveals the potential for nanofluids, particularly those incorporating TiO2 nanoparticles, to significantly enhance the cooling efficiency of VCRS. These findings have important implications for the design and optimization of VCRS systems, ultimately contributing to reduced energy consumption and environmental impact.
Downloads