Estimation of Potential Evapotranspiration using Multiple Linear Regression and Particle Swarm Optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.126.1.8190Keywords:
Potential evapotranspiration, multiple linear regression, particle swarm optimizationAbstract
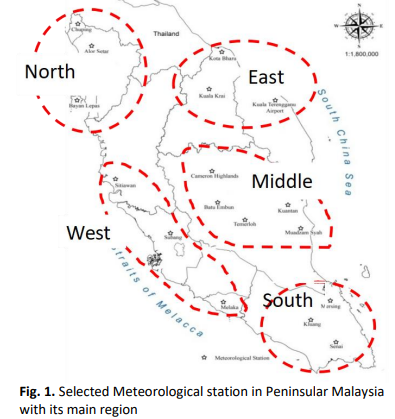
The study of estimating potential evapotranspiration (ETp) in managing water resources for domestic, agricultural and irrigation purposes in Malaysia is considered lacking. Not only study on ETp provides valuable insight on water cycle management, but also helps in predicting the water demand and optimize the agricultural practices. Hence, this study evaluates the performance of developed ET estimation model using MLR algorithm and optimized by PSO algorithm for five main region in Peninsular Malaysia using historical data from 1987 till 2003. The developed ETp models (MLR-ET) were then optimized (MLR-PSO) using PSO algorithm. Results show that the performance of MLR-ET for R2 ranging from 0.897 to 0.987 where MBE value is from 0.04 to 0.19, PE range is between 1.8 to 5.3 and RMSE is range between 0.20 to 0.30. Whereas for MLR-PSO models, performance (R2) ranging from 0.942 to 0.993 MBE value was from 0.12 to 0.20, PE range is between 0.4 to 4.0 and RMSE ranged between 0.14 to 0.33. The performance of RMSE, MBE and PE indicators for MLR-ET were better than MLR-PSO yet the performance of R2 for MLR-PSO models were better. Nonetheless, both MLR-ET and MLR-PSO models are reliable as the results of performance indicators lies within appropriate limits.
Downloads