Heart Disease Prediction of Cleveland Clinic Patients using Advanced Machine Learning Algorithms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.126.1.114Keywords:
Heart disease patient, prediction, machine learning algorithms, XGBoostAbstract
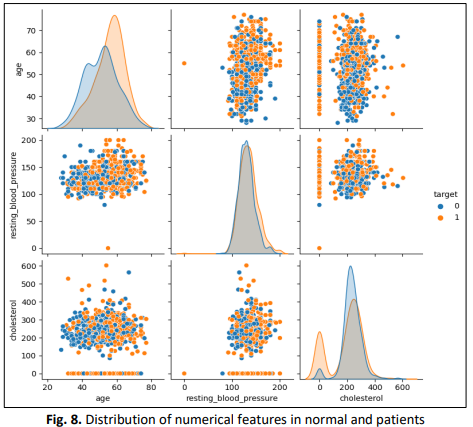
Globally, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) constitute the primary cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Early diagnosis of those at risk of CVDs may lower the number of avoidable fatalities. It has been shown that machine learning (ML) is helpful in anticipating cardiac issues. Adoption of a prediction system that can detect cardiac diseases before they deteriorate would offer people worldwide enormous hope and help in decision-making. ML has become a popular technique for generating predictions from enormous real-world datasets. It has also been discovered that many ML classifiers contain issues and flaws. However, the latest ML algorithm from the boosting family, i.e., XGBoost, may enhance performance and assist in exact prediction. As a result, this study will compare XGBoost to other prominent classifiers in terms of their capacity to anticipate and improve performance. ML classifiers, such as Multilayer Perception, K-nearest neighbours (K-NN), Support Vector Classifier, CART and XGBoost algorithms, are used to differentiate between healthy and CVD patients. When compared to competing classifiers, the XGB classifier achieves 89% accuracy, 87% precision, 94% sensitivity, 94% specificity, 90.2% F1 score, 81.2 % ROC, 78.90% Mathew coefficient and 3.87% log loss. In the future other ML classifiers such as Random Forest, Multilayer Perceptron, K-nearest Neighbor, Extra Tree Classifier, Extreme Gradient Boosting, Support Vector classifier, Stochastic Gradient Descent, AdaBoost, Classification and Regression Tree and Gradient Boosting along with these algorithms could be applied to compare the MLA efficiency.
Downloads