Effect of Cement Plaster and Insulation Materials on the Thermal Performance of Masonry Wall
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.123.1.248260Keywords:
Insulation material, clay brick, Thermal performance, masonry wallAbstract
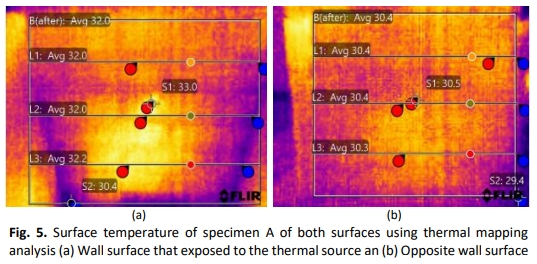
The thermal performance of masonry walls plays a critical role in maintaining indoor comfort and minimizing energy consumption. However, in many developing countries, construction practices often overlook the importance of thermal insulation and mass, leading to inefficient energy use in buildings. This study investigates the effect of cement plaster thickness and insulation materials on the thermal properties of masonry walls constructed from clay bricks. The primary objective is to assess how varying plaster thickness and the inclusion of insulation materials impact thermal conductivity and heat transfer. Two methods were employed for data collection: the use of thermocouples to measure spot temperature differences and a thermal imaging camera to create surface temperature maps. The findings reveal that thicker cement plaster and insulation materials, particularly polystyrene boards, enhance the wall's thermal resistance, reducing heat transfer. Specifically, a 20mm polystyrene board reduced heat transmission by up to 51.7%. These results underscore the importance of integrating effective insulation materials in building design to promote energy efficiency and improve thermal comfort. Further research into innovative insulation solutions is recommended to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness.
Downloads