Effects of Surface Roughness on Friction Factors in Circular Galvanized Steel (GS) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Tubes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.123.1.243247Keywords:
Turbulent flow, friction factor, surface roughness, Reynolds numberAbstract
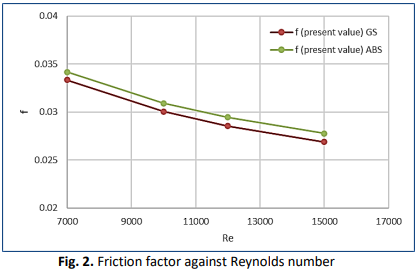
The study of friction losses in pipes used in engineering and industry is important to improve flow efficiency and reduce the energy required to transport fluids. The surface roughness of a pipe affects its friction coefficient and its efficiency and performance. This numerical study explores numerically the impact of surface roughness on friction factors in circular tubes made of three distinct materials. The research employs computational fluid dynamics (CFD) ANSYS Fluent software to simulate turbulent flows, incorporating various surface roughness models in Galvanized steel (GS) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) circular tubes. The simulation setup encompasses tube geometry, fluid properties, and boundary conditions. The simulation setup involves the pipe shape, fluid characteristics, and boundary conditions. The results indicate a precise link between surface roughness and friction factors, providing insights into pressure drop and flow characteristics. Validation against experimental data and known correlations enhances the dependability of the results. The findings help to optimise fluid transport systems and open the way for future study in this important technical subject. The friction factor decreases consistently with the increasing Reynolds number, and it is lower than the theoretical value. Galvanized steel (GS), with an absolute roughness of 0.15 mm, exhibits an 8% higher friction factor compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). This validation of the experimental data and known correlations enhances the reliability of the results.
Downloads