Assessment on Tracking Performance of PID, Cascade Proportional Adaptive Interaction Algorithm and Nonlinear Adaptive Interaction Algorithm Controller of XY Table Ball Screw Driven System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.141.1.7489Keywords:
PID, cascade proportional adaptive interaction algorithm, nonlinear adaptive interaction algorithm, xy table ball screwAbstract
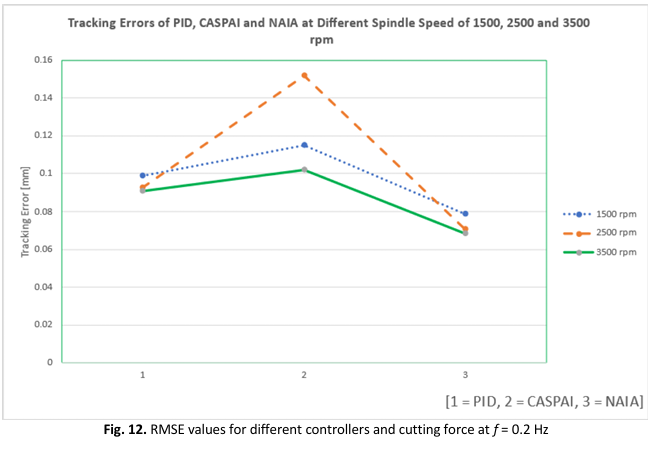
Recently, the major focus in machine tools has been on achieving precise positioning, robust monitoring, low-cost manufacturing, and adaptability to disturbances. These recent demands, or paradigm changes, have ushered in a new and complicated era for machining tools and controls. This paper presents a new technique and contribution to compensating cutting force disturbances using the Nonlinear Adaptive Interaction Algorithm (NAIA). The NAIA controller is created by adding a modified nonlinear function to the main Adaptive Interaction Algorithm Controller (AIA) controller. First, the mathematical model of a machine tool for an XY table is identified using a system identification approach based on the system's frequency response function. Secondly, a new control strategy that will provide good tracking performance of the XY table is designed. Then, the proposed technique through simulation using MATLAB/Simulink software and experimental work using a real plant of Googoltech XY table. It successfully demonstrated that the tracking performance of a machine tool was increased significantly through the newly proposed technique that was compared with the basic PID controller. The results indicate that the newly suggested NAIA control approach succeeded in achieving up to 60.2% improvement in comparison with PID (frequency, f = 0.6 Hz) and 53.55% improvement. in comparison with CasPAi (at f = 0.2 Hz). In addition, results showed that the NAIA provides an improvement of 86.29% in terms of Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) for f = 0.6 Hz in comparison with Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) and a 78.68% improvement in comparison with CasPAi.
Downloads