Temperature Effect in the Calibration of NIS Reference Humidity Sensors Using a Two-pressure Humidity Generator
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.123.1.18Keywords:
Temperature effect, humidity sensor, two-pressure humidity generator, calibration, correlationAbstract
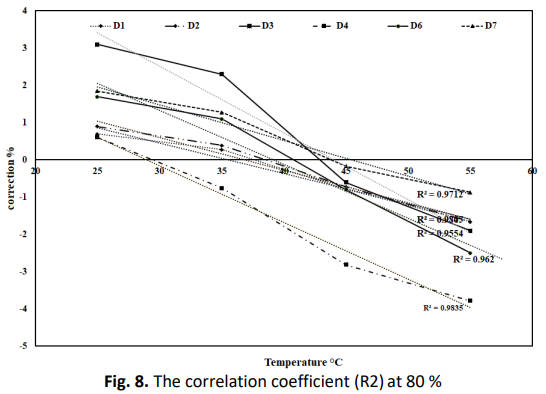
Humidity sensors play a vital role in massive production technology and are widely used in industrial processes, medical facilities, museums, agricultural settings, food preservation, meteorology, etc. This paper describes the study of the effect of temperature on different humidity sensors used in practice. The analysis and findings of a study on the role of temperature in the calibration of humidity sensors are presented in this paper using a two-pressure humidity generator (2-P). Relative humidity measurements were performed at different humidity levels: 10, 30, 50 and 80 %. The temperature was adjusted at different setpoints: 25, 35, 45 and 55 °C. The data and associations were assessed using pythonic statistical software. The results show that humidity correction is contingent on the temperature and device used when considering certain conditions. The calibration correction is independent of the temperature for temperatures ranging from 25 to 35 °C, but the calibration correction is strongly dependent on the temperature for conditions above 35 °C in the range from 30 to 80 % relative humidity. The effect of temperature on the calibration of seven hygrometer models was evaluated using the humidity standard in the thermal metrology laboratory at the National Institute for Standards. The results showed that there is a strong correlation between temperature and humidity. The difference in the humidity correction factor shown from the results in this paper was applied during the calibration processes to ensure accuracy and improve measurements in the thermal metrology laboratory at the National Institute for Standards.
Downloads