The Assessment of Solar Powered Green Campus vs The Conventional Approach: A Case Study at the Main Campus of Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.118.1.2033Keywords:
Green building, energy consumption, solar powered, energy efficiency, electricityAbstract
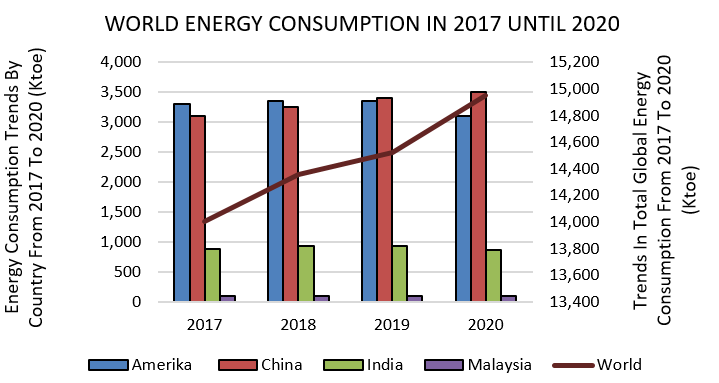
As a guarantee that Malaysia practices sustainable development, this matter is important to be approached in detail and proactively as it guarantees a better future change. The concern of many people including educational institutions is not only to be able to preserve the environment but also to be able to manage the institution's budget expenses and provide satisfactory well-being to the people of Universiti Sains Malaysia. Achieving stability is an important endeavor, encompassing both private and public structures, with a particular focus on educational institutions. This study aims to understand in detail about the effectiveness of solar use in energy saving efforts compared to the use of conventional approaches to meet the term green campus in educational institutions. This objective is in line with the aim of this research which is to evaluate the annual electricity bill in Ringgit Malaysia (RM) main campus of Universiti Sains Malaysia, to analyze the difference in electricity before and after the use of solar energy is practiced on buildings at Universiti Sains Malaysia and the final objective is to give recommendations for productive and efficient electricity saving measures that can be done on campus. This research uses qualitative as a data collection technique to obtain information about electricity and energy consumption at USM. The results of this study will increase the understanding of the effectiveness of solar use in reducing the cost of electricity in a building and give a larger and specific picture of the energy savings that need to be done to maintain the term of green building in the aspect of energy efficiency in educational building.
Downloads