Design Microstrip Bandpass Filter from 2 GHz to 4.7 GHz for Biomedical Applications
Keywords:
Microstrip patch antenna, bandpass filter, wireless communication systems, biomedical applicationsAbstract
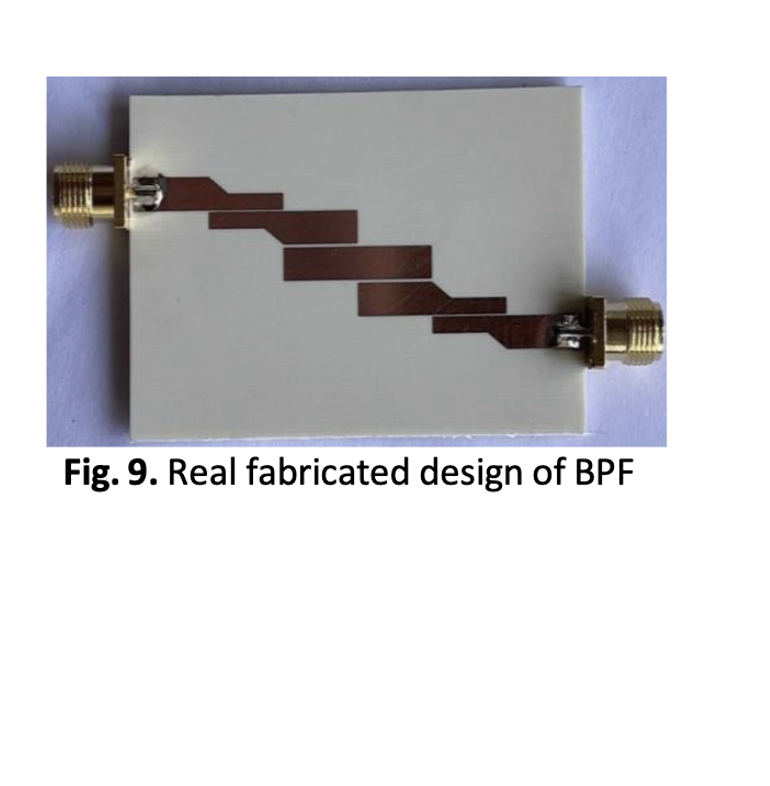
The paper's aim was to demonstrate the design methodology, fabrication of a genuine prototype, parameter analysis and measurement findings in comparison to modelling of a 5.8 GHz rectangular parallel linked microstrip patch antenna. The findings of the simulation research, practical measurement and antenna design calculations were given and contrasted. This study will be beneficial for producing a low-cost 5.8 GHz rectangular microstrip patch antenna and investigating the parameter studies. The shared knowledge was intended to make system features better. A significant part in wireless communication systems is played by band pass filters. It is necessary to filter sent and received signals at a specified frequency and bandwidth. In this study, Computer Simulation Technology (CST) was applied to build and simulate a microstrip parallel coupled-line band pass filter with a broad bandwidth of 1.25 GHz running at a centre frequency of 3.9 GHz. The suggested bandpass filter was set at 3.861 GHz by modifying the width between the linked lines, and at 3.926 GHz by adjusting the gap, with dimensions of 60 mm x 30 mm. The filter had a 1.25 GHz bandwidth with a -3 dB insertion loss, -17.3 dB return loss and a -2.2 dB bandwidth. The results addressed how the linked line's width and gap affect its centre frequency.
Downloads