Modelling and Simulation of Graphite Synthesis via Hydrochloric Acid Leaching
Keywords:
Simulation, graphite synthesis, MATLAB, hydrochloric acid leachingAbstract
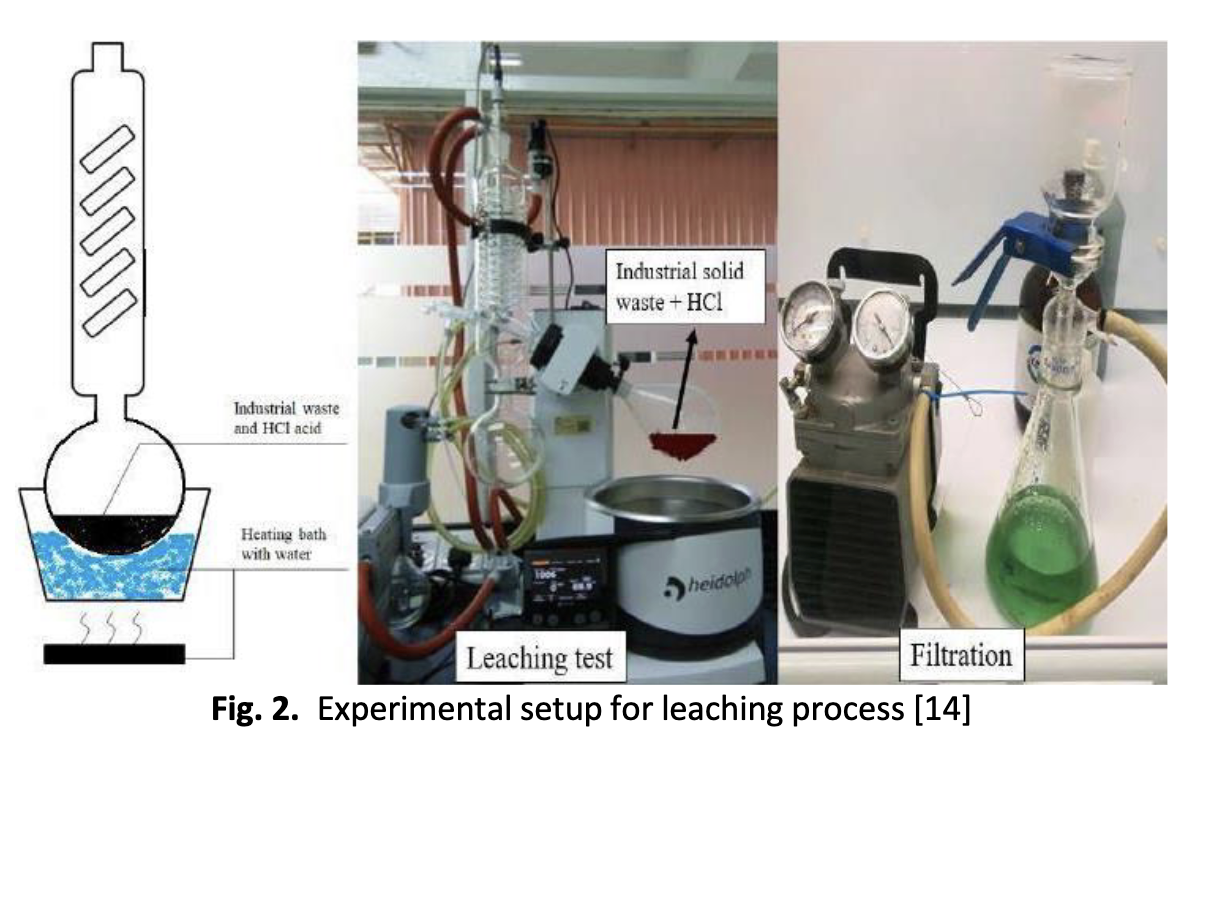
In this study, a simulation model of the synthesis of graphite from industrial waste via acid leaching was developed in MATLAB. The results obtained from this simulation will help contribute towards the preliminary understanding of large scale production of graphite. The acid leaching of industrial waste was carried out with the aid of HCl as the leaching agent based on 4 factors namely the concentration of HCl (A), temperature (B), solid to liquid ratio (C) and leaching time (D). Next, a statistical analysis was done via Response Surface Methodology (RSM) which is commonly used for modelling and optimization studies. Twenty-seven experimental runs were done based on the 4 factors on 3 levels of CCD. The ANOVA model and response surface plots were generated. ANOVA analysis was used to study the importance of each factor for the percentage of metal removal. The F-value and p-value of 68.17 and <0.0001 respectively were significant with the leaching model. The R2 value of 0.99 and Adj-R2 value of 0.97 were used to prove the fitting of the model. From the ANOVA model, a quadratic equation was attained and this equation was used for the simulation model. The simulation model was then done via Simulink in MATLAB and based on the optimum parameters the simulation was run. From the findings, variable A did not show any changes in the metal removal percentage. As for variable B, C and D the highest metal removal percentage was obtained at temperature of 70 degree celsius, a solid to liquid ratio of 10:1 and a leaching time of 60 mins, respectively
Downloads