Optimization of Parameters for Polydiacetylenes Vesicles using Response Surface Methodology as a Function of Calorimetric Sensor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.114.1.19Keywords:
Polydiacetylenes vesicles, optimal condition, optical absorbance, response surface methodologyAbstract
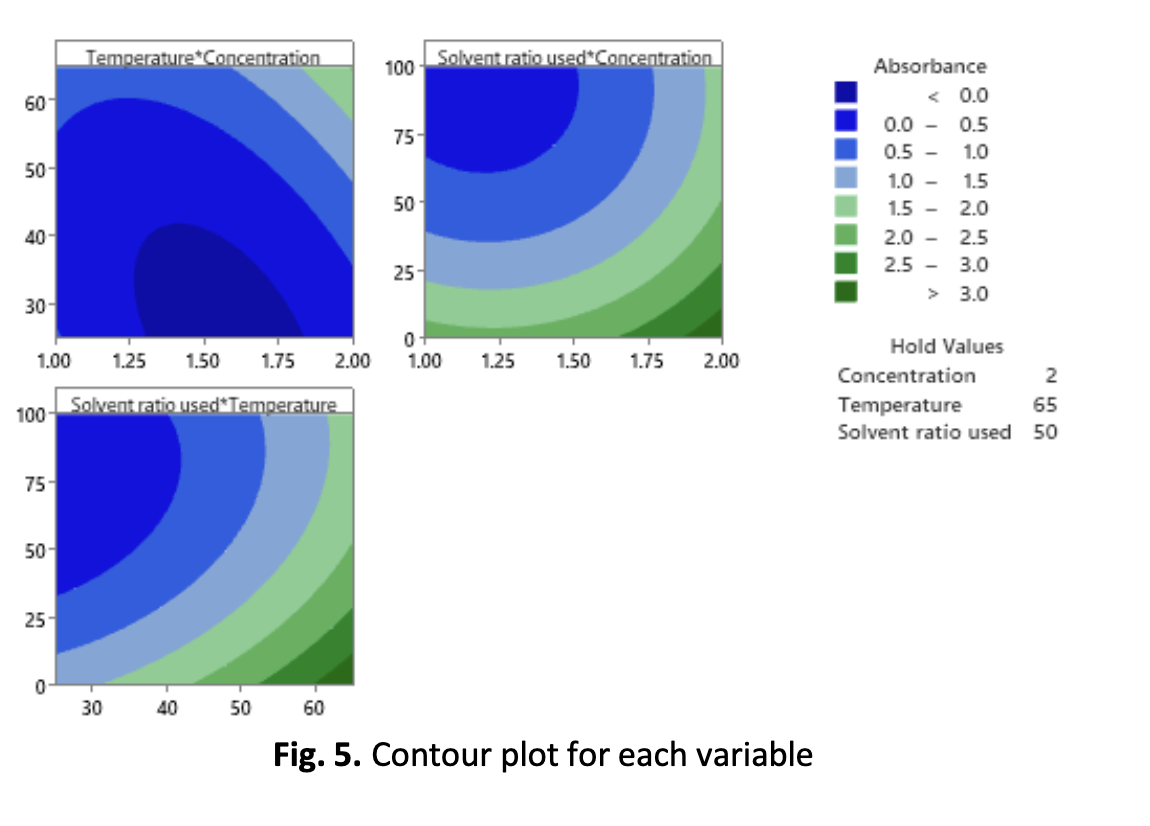
Polydiacetylenes (PDAs) are well-known materials that can be used as colorimetric stimulations sensors. PDA-based materials are usually produced though the self-assembly in an aqueous solution. Since the responses of PDA vesicles produced under different conditions changed, the PDA vesicles must be optimized. It was employed to optimize the irradiation dosage, concentration, temperature and solvent ratio for PDA vesicles by using the Box-Behnken experiment design. Box-Behnken Design (BBD) can help reduce the number of tests needed by analyzing several combinations of variable levels at the same time. The peak of optical shift characteristics of PDAs vesicles was enhanced in parallel with the optimization of optimal parameters. As a consequence, the conditions with the maximum optical absorbance as evaluated by UV-Vis Spectroscopy were preferable. Therefore, the results indicate that this model is reliable and can precisely identify the maximum response peak. It was concluded that the BBD experimental design concept could be effectively used to optimize the parameters for the formation of PDAs vesicles with the fewest number of experimental runs possible. The PDAs vesicles formed under these conditions will be used for further characterization and testing. As a consequence, the best optimal conditions for 10,12-pentacosadyinoic acid (PCDA) vesicles can be concluded at 2.0 mM monomer concentration, 65 degree celsius processing temperature and 50:50 solvent ratio used between chloroform and tetrahydrofuran.
Downloads