Decolourization of Methylene Blue by Resting Cells and Immobilized Cells of Rhodococcus Strain UCC 0003
Keywords:
Decolourization, immobilization, Methylene blue, resting cells, Rhodococcus strain UCC 0003 strain, textile IndustryAbstract
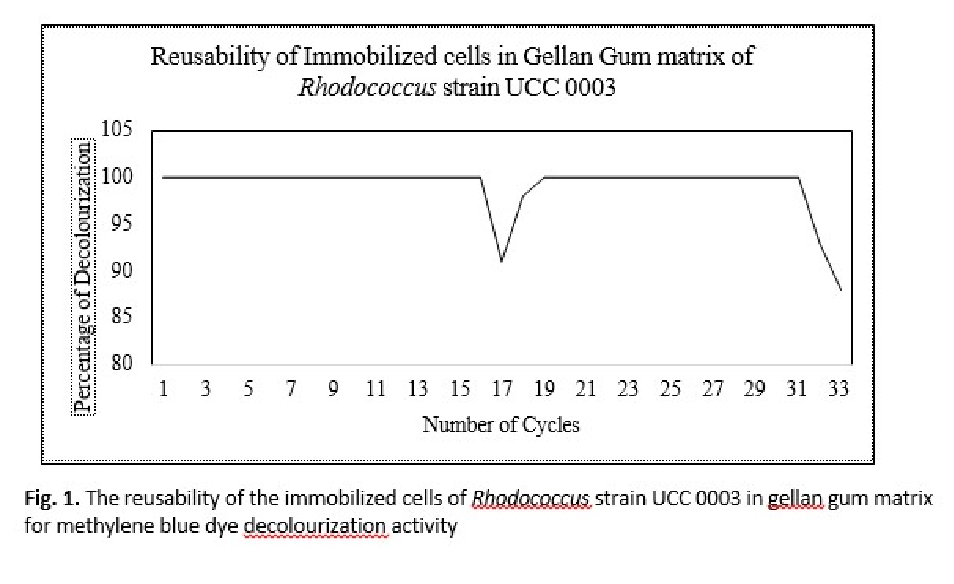
Methylene blue is extensively used in printing and batik industries in Malaysia. The increase in usage of coloured dyes which are toxic and long lasting in the natural environment can affect the water quality. Thus, there is a worthy technique which was developed as a cheaper way to achieve desired environment without hazards. The current study investigated the use of locally isolated Rhodococcus strain UCC 0003 for methylene blue dye decolourization. The decolourization of methylene blue dye was carried out in the two different modes namely resting cells and immobilized cells of Rhodococcus strain UCC 0003 in gellan gum matrix. The methylene blue removal using resting cells and immobilized cells after 24 hours of incubation resulted in 38 % and 73 % decolourization, respectively. Further characterization was proceeded with immobilized cells in gellan gum matrix to evaluate the potential of repeated use of the biocatalyst. The reusability of immobilized cells of Rhodococcus strain UCC 003 was carried out for 17 repeated cycles. The first cycle was initiated by adding 50 mL (0.5 g/L) of methylene blue solution in the Erlemeyer flask that contained 50 beads of gellan gum. The first 16 cycles resulted in complete decolourization within an hour incubation period for each cycle. Meanwhile at the 17th cycle, the decolourization efficiency dropped to 91%. This trend was repeated when fresh cells of Rhodococcus strain UCC 0003 immobilized in gellan gum were tested to decolourize 0.5 g/L of methylene blue. These findings clearly proposed that immobilized cells of Rhodococcus strain UCC 0003 in gellan gum matrix has huge prospects to remediate the industrial wastewater since the biocatalyst could be reused which optimized the cost and method is environmentally acceptable.
Downloads