The Significant Effect of Graphene on Inorganic Salt Hydrated Phase Change Material Thermal Physical Enhancement
Keywords:
Phase change material (PCM), calcium chloride hexahydrate, thermal physical properties, grapheneAbstract
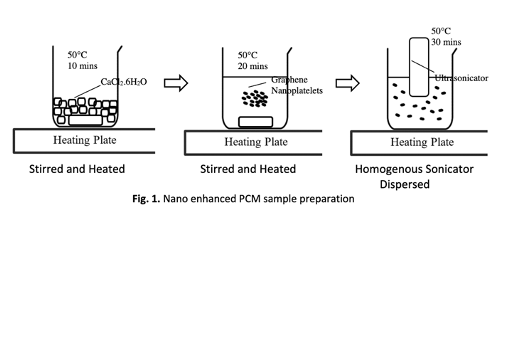
In this experimetal study, inorganic salt hydrated phase-change material (PCM) based on Calcium Chloride Hexahydrate (CaCl2·6H2O) was employed to characterize phase change behavior such as the supercooling degree, phase change temperature and thermal conductivity. The CaCl2·6H2O nanocomposite PCM contained with different volume fraction (wt.%) of Graphene Nanoplatelets (GNP) are verified by heatingcooling curves resulted in enhancing thermal behavior. Results demonstrate the validation phase change temperature of the CaCl2·6H2O pure PCM are significantly referenced, while thermal conductivity and supercooling of CaCl2·6H2O/GNP nanocomposite PCM was observed. The degree of supercooling is within the range of 6.0-15.2°C, with the maximum reductions of 68% and no phase segregation was observed. The thermal conductivity of the CaCl2·6H2O/GNP with 1.0 wt.% 14.4% was higher than 0.5 wt.% of GNP. The CaCl2·6H2O/GNP nanocomposite PCM presented acceptable thermal reliability and heat transfer characteristics, thus imitates its prominence for low-temperature range thermal energy utilization.
Downloads