On the Application of Nanofluid in Minichannel for Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Analysis
Keywords:
Nanofluid, Minichannel heat sink, convective heat transfer, pressure drop, aspect ratioAbstract
Heat transfer and flow of fluids are processes that are prevalent in thermal engineering. They occur in many aspects of energy utilization and management. Rapid technological advances in electronic devices through reduction of sizes or simply miniaturization leads to the development of integrated circuits of ultra-large-scale magnitude (ULSIC) as new generation high-performance dense module, but with a consequence on increase power density and extremely intense heat flux which hampers on the long-term reliability and efficiency, as well as reduction of mean time between failure (MTBF) of electronic devices. Conventional fluids failed to provide required heat removal from high heat flux generating electronic devices and heat exchangers, due to their inherent low thermal conductivity. Nanofluid is an advance innovative thermal engineering fluid capable of providing outstanding heat transfer improvement than the conventional fluids, thus, increasing thermal system productivity and ensure energy sustainability. The Micro (MC) and minichannels (MiC) are the preferred state-of-the-art transport passage nowadays and are receiving much attention from researchers. They differ from conventional channels for having a
hydraulic diameter in the range of 0.01 – 0.2 mm and 0.2 – 3 mm for micro and minichannels, respectively. In this paper, the various recent experimental and
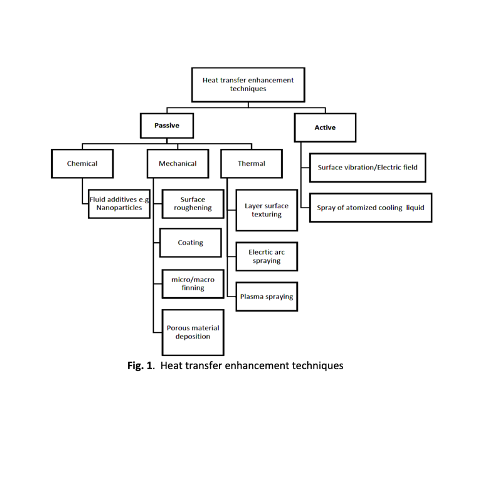
numerical works on utilizing nanofluids in minichannels are reviewed and summarized with emphasis on heat transfer enhancement mechanisms and techniques employed, achievement of thermal improvement, and various thermal engineering applications.
Downloads