Hydrothermal Performance in a New Designed Hybrid Microchannel Heat Sink with Optimum Secondary Channel Geometry Parameter: Numerical and Experimental Studies
Keywords:
Hybrid microchannel heat sink, secondary channel, optimal parameter, heat transfer, low Reynold numberAbstract
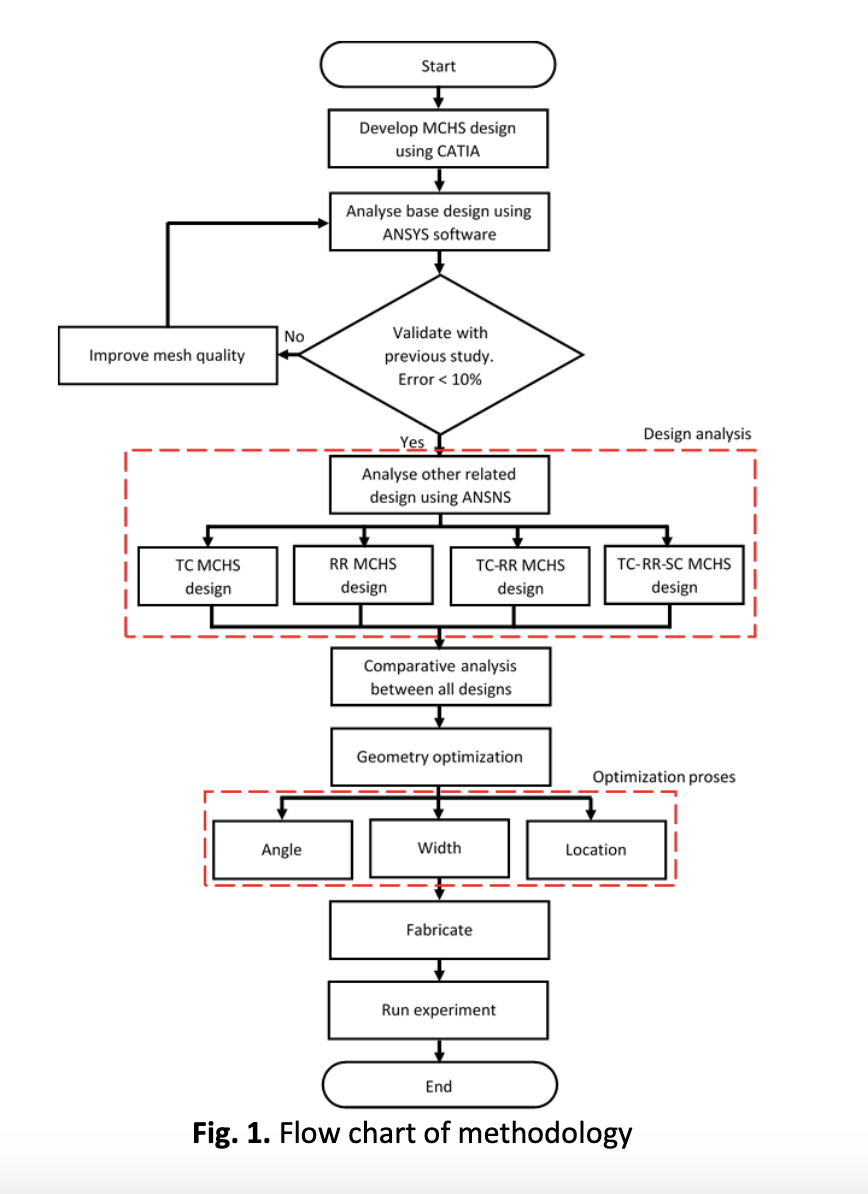
Miniaturization and utilization of low-dimensional structures of recent electronic devices have witnessed some new micro cooling methods which can fulfil the cooling demand for the electronic devices. Microchannel heat sink (MCHS) is one of the micro cooling method which appears as a promising method that can provide high heat transfer rate due to small hydraulic diameter. Furthermore, microchannel heat sink is easy to fabricate compare to other micro cooling methods. Due to fast development in electronic industry, hybrid microchannel heat sink with optimal design has received a great deal of attention in order to provide high heat transfer performance with acceptable pressure drop. However, most of the acceptable pressure drop has required high pumping power due high friction factor at high Reynold number in a proposed hybrid design. Therefore, the aim of this article to propose a new hybrid microchannel heat sink which can obtain the high heat transfer performance with minimal friction factor at low Reynold number by introducing optimum secondary channel geometry parameter in cavities-ribs microchannel heat sink. In this study, comparative analysis was conducted between proposed hybrid design with other
related designs. Besides that, optimization of secondary channel geometry was conducted in order to achieve high heat transfer rate at low Reynold number. The comparative analysis revealed that secondary channel that connected between adjacent main channel increased the degree of flow mixing which contributed to the enhancement of heat transfer performance. Besides that, proposed hybrid design with optimum geometry parameter of secondary channel achieved the high overall performance at low Reynold number.
Downloads