Municipal Solid Waste Characteristics in Taman Universiti, Skudai, Johore, Malaysia
Keywords:
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), waste component, waste managementAbstract
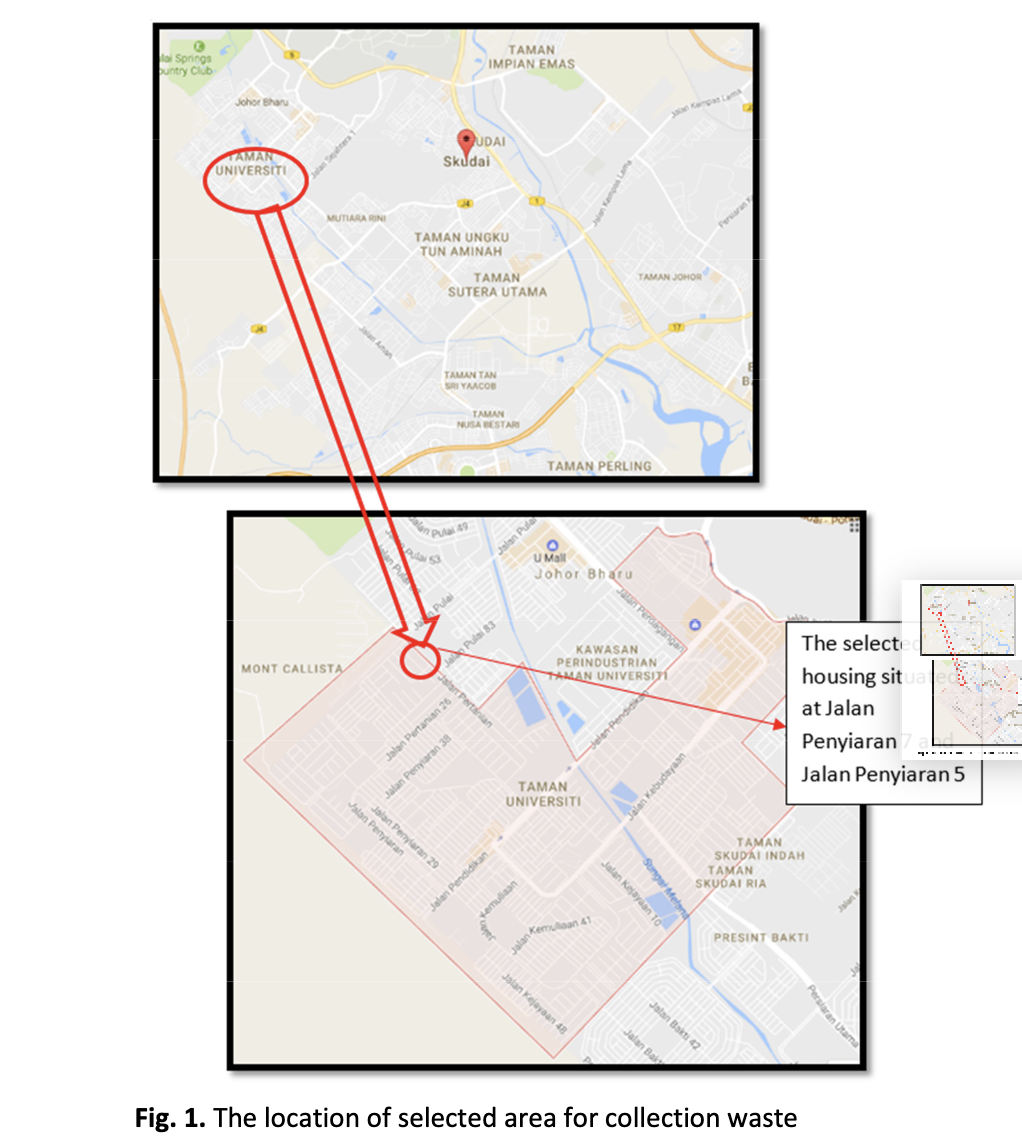
Malaysia is one of the developing countries that are facing an increase population with an increasing and significant generation of waste. Environmental problems may arise when the solid waste management is improper. The rate of generation is increasing and the composition is also changing as the nation becomes more urbanized and industrialized. The objective of this study is to present the data of municipal solid waste (MSW) generated in Taman Universiti, Skudai, Johor Bahru, Malaysia. The composition of MSW was studied by segregating it into different components such as food waste, paper, glass, plastics, metal and tin aluminums. It was observed that Taman Universiti area produced around 40% plastics waste which was the highest component compared to other waste, followed by food waste and papers with 38.2% and 21% respectively. Meanwhile, food waste was recorded the highest moisture content with 38.2% while glass had the lowest moisture content with 0.4%. The reliable estimate of MSW generated is important for proper waste management planning. These data could enhance in implementation of waste management system in that area.
Downloads