Classification of Malaysian Honey Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis
Keywords:
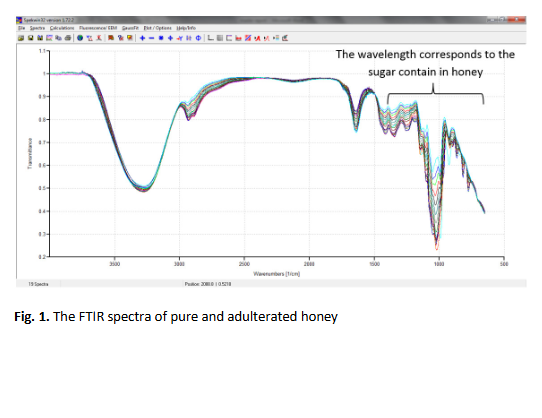
Chemometric analysis, spectroscopic technique, FTIR, pure and adulterated honeyAbstract
Honey is a natural sweetener, which is consumed in a variety of sweet products. It is considered as healthy food because it contains nutrients such as carbohydrate, protein, vitamins and mineral. The presence of adulterated honey in the market is worrying the consumers since it is difficult to distinguish between pure and adulterated honey due to similar appearance and texture of both type honeys. Chemometric analysis combined with spectroscopic data is a powerful technique that has been used to discriminate different type of honey. Samples of pure honey are collected from beekeepers at Ayer Keroh, Melaka and Cameron Highland, Pahang. The adulterants used to prepare adulterated honey are sugar and corn syrup with the concentration of the adulterants added to the pure honey ranging from 10% to 90% by weight of adulterant. All the samples are treated with heat at 40o C to ensure the adulterant and pure honey are mixed well. Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is used to generate the spectra of the honey and subsequently subjected to chemometric
analysis. The spectra data is then analysed by using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) technique using SOLO+Mia software. In this study, all honeys have been successfully discriminated according to their origins and purity as well as types of adulterants used. Consequently, the developed model can potentially be used as a screening tool to determine the purity of honey in the market.
Downloads