Factors Influencing the Success of Vaginal Birth After Caesarean Section in Sarawak General Hospital 2010
Abstract
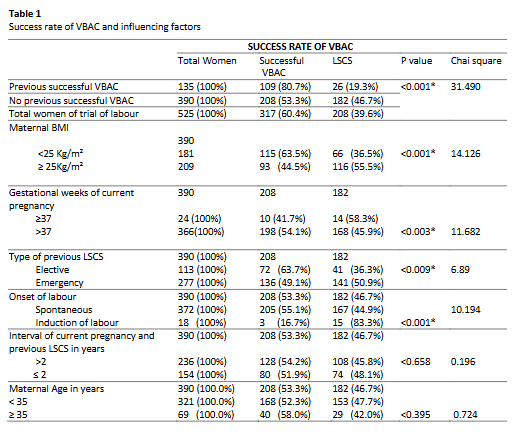
The research was conducted to study influencing factors for successful vaginal delivery after caesarean section (VBAC) among women delivering at Sarawak General Hospital, Malaysia in 2010. It was a hospital based retrospective study in maternity unit, Sarawak General Hospital, Malaysia, among pregnant women with one previous lower segment caesarean section for trial of vaginal delivery during 2010.This study was carried out in through the antenatal, intrapartum and postnatal records. During the study period, a total of 525 pregnant women with one previous lower segment caesarean section scar were admitted for a trial of vaginal birth. Among 525 women, 390 did not have a prior history of successful VBAC and the remaining 135 women had at least one successful
VBAC. Overall there was a successful VBAC rate of 60.4%. The success rate among women who had previous successful VBAC was 80.7%; while for those who had no prior history was only 53.3%. Influencing factors are studied among 390 women with one previous caesarean who did not have a prior history of successful VBAC. In the group of women whose body mass index (BMI) was > 25 Kg/m2 , the successful rate was lower at 44.5% when compared to 63.5% among women with a BMI <25 Kg/m2 with a P value <0.000, [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.4-3.1]. The successful VBAC rates vary according to the gestational age of the pregnancy. The successful VBAC rate was 41.7% among women who were less than 37 weeks of gestation and 54.1% among those with gestational age 37 weeks and above. These were statistically significant with a P value -0.003, [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.3-0.8]. It is interesting to note that if the
previous lower segment caesarean section was an emergency, the successful VBAC rate was 49.1% compared to 63.7% if it was an elective procedure. (P value= 0.009), [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.3-3.4]. Induction of labour reduced the successful rate of vaginal delivery in trial of labour. If labour was spontaneous, the successful VBAC rate was 55.1% compared to 16.7% in women who were induced into labour. (P value -0.001). The study concluded that previous successful VBAC, body mass index (BMI), gestational age, the type of previous lower segment caesarean section and induction of labour were significant factors in influencing the rate of successful VBAC.
Downloads