Sedimentation Analysis for Uncured Magnetorheological Elastomer for Potential Additive Manufacturing using Vat Photopolymerization Technique
Keywords:
Additive manufacturing, Magnetorheological elastomer, Sedimentation, Vat photopolymerizationAbstract
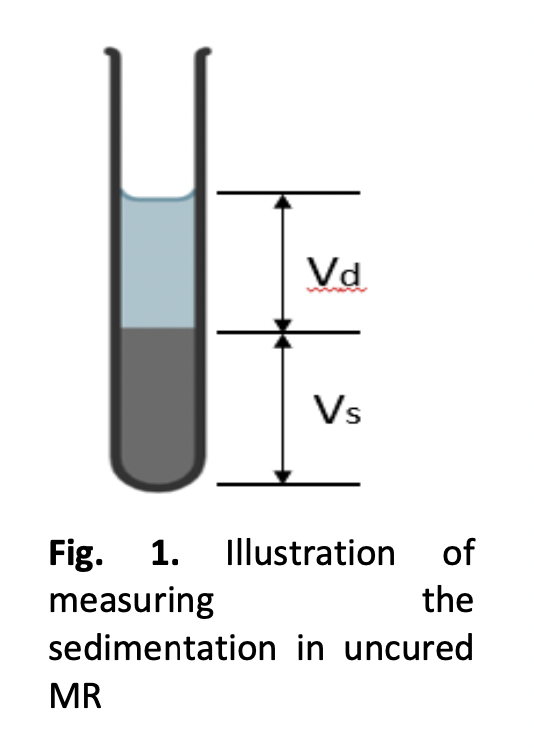
Additive manufacturing using vat photopolymerization technique is one of the potential techniques to fabricate magnetorheological elastomer (MRE). However, due to the density mismatch between the elastic resin and magnetic particles for the preparation of the uncured MRE leads to sedimentation problem. Therefore, this study investigates the sedimentation behaviour between the photopolymer elastic resin and carbonyl iron particles (CIPs) in the uncured MRE. The uncured MREs were prepared in different weight percentage (wt.%) of 30, 40, 50 and 60 wt.% of CIPs. The result demonstrated that all wt.% of CIPs compositions has started to simultaneously sediment about 3 hours. The uncured MRE with 60 wt.% of CIPs has produced the lowest sedimentation ratio (50%), indicating the lowest sedimentation rate to settle at the base of the test tube after 24 hours. Therefore, the outcome of this study has deduced that sedimentation has occurred in the uncured MRE and this analysis provides prediction on the fabrication of MRE by vat photopolymerization technique.