An Observational Study on Motorcycle Crossing Pattern at Three-Legged Signalised Junction in Malaysia
Keywords:
Motorcycle safety, motorcycle path, three-legged junctionAbstract
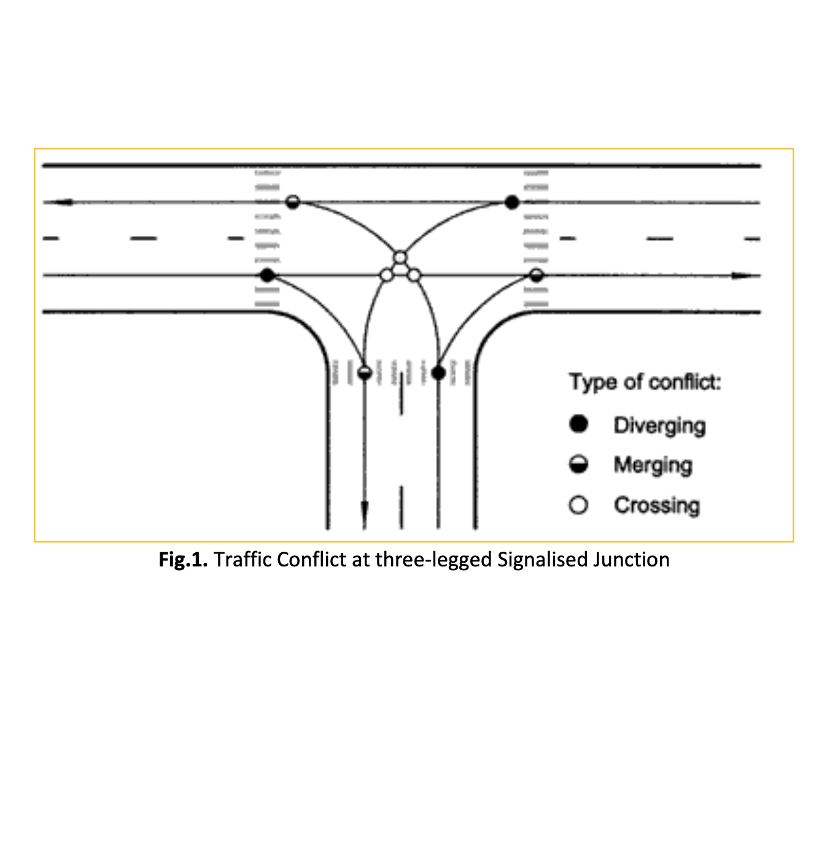
Traffic signals are a common form of traffic control used by road authorities and local agencies all around the world to manage traffic movement at a junction. In 2012, 18.5% of all fatalities and injury collisions in Malaysia occurred at intersection. Many motorcycle fatalities occurred within intersections after a driver failed to see a motorcyclist. However, little is known about the behaviour of motorcyclists when they negotiate at intersection. This study was undertaken to analyse the behaviour of motorcyclist when crossing the three-legged signalised junction. Motorcycle path data were observed at three (3) signalised junction in peninsular Malaysia during peak and off-peak hour period. Motorcycle path in this study defined as to the path taken by the motorcycle when they start moving from one (1) leg to another leg of the junction This study grouped motorcycle path into turning and straight movement. Findings shows for turning movement 46.5% motorcycle executed a changing lane while for straight movement shows only 17.4% executed a changing lane to complete crossing maneuver. The disorderly movement by motorcycles creates traffic conflict at the junction and may lead to a crash. By following the actual path, motorcyclist may reduce the contact point with the other vehicles especially at intersection.