Hospital Preparedness towards Earthquake in Malaysia: A Quantitative Approach
Keywords:
Hospital, disaster preparedness, earthquake, descriptive statistic, relative importance indexAbstract
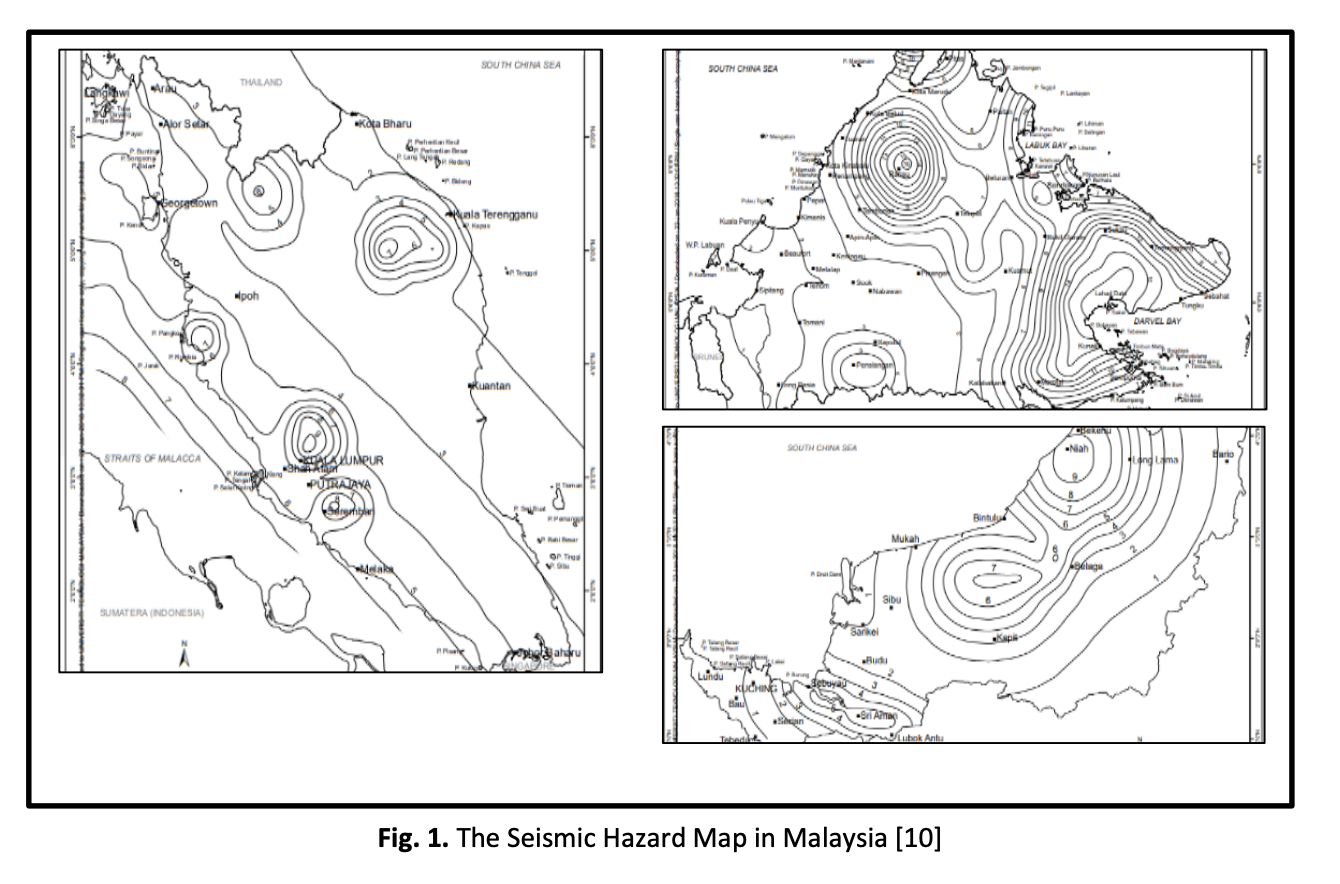
Malaysia located outside the ‘Pacific Ring of Fire’ and considered to be safe from any seismic activities. However, tremors were felt in some areas due to far-field and near-field earthquake effects. Hospitals are important for any post-disaster event and maintain their resilience in any situation. The objective is to evaluate the level of preparedness for earthquakes in Malaysian hospitals. This cross-sectional study using purposive sampling to find the minimum sample size and snowball technique for distributing the questionnaire via Google form. A descriptive statistics and relative importance index were used for the analysis. Total of 144 respondents involve in this study among health personnel and civil servants working in hospital and healthcare facilities in Ministry of Health Malaysia. Based on the results, it is shown that the level if preparedness of hospital towards earthquake are in the modest level Mean= 3.506-3.893. There is a need to have a building and facilities safety RII=0.825 as the first rank for preparedness towards earthquake disaster compared to emergency stockpiles logistics and coordination RII=0.815, disaster training and education RII=0.814, emergency support competence RII=0.804, human resources leadership RII=0.804, stress-coping ability RII=0.779 and work continuity competence RII=0.767. This study provides the importance of a safety building as the first priorities in preparedness towards earthquake in Malaysia and the importance of having a hospital with seismic design model for facing any disasters in future.