A Novel Investigation on Microstructural Analysis of a Rupture GRE Composite Pipe for Underground Fire Water System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.23.1.3548Keywords:
GRE pipe, rupture, microanalysisAbstract
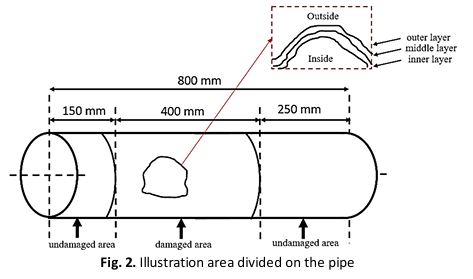
This study investigates how underground fire water systems using Glass Reinforced Epoxy (GRE) pipes are affected by aging. Over time, GRE pipes can degrade, potentially reducing their expected lifespan. The study compared damaged and undamaged areas of pipes to assess how damage impacts their structural integrity. Microscopic and chemical analyses (SEM and EDX) were performed on pipe samples from different locations of the pipe. Mechanical testing (following ASTM standards) was conducted beforehand. Analyses revealed that as damage increased (closer to damaged area), the levels of carbon (C) and oxygen (O) changed significantly with the weight percentage exposed 45.62% difference and 11.62% difference, respectively, as compared with the undamaged area. This suggests that the epoxy resin degrades with age, releasing these elements. Additionally, the presence of foreign objects around the pipes can affect how they bear loads. These findings highlight the importance of understanding how aging and surrounding conditions can influence the performance of GRE pipes in real-world fire water systems.