Systematic Review on Indoor Microplastics: Unveiling Sources, Exposure Pathways, and Human Health Implications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.20.1.96111Keywords:
Microplastics, indoor environment, human health, exposure pathways, SDG 3, SDG 11Abstract
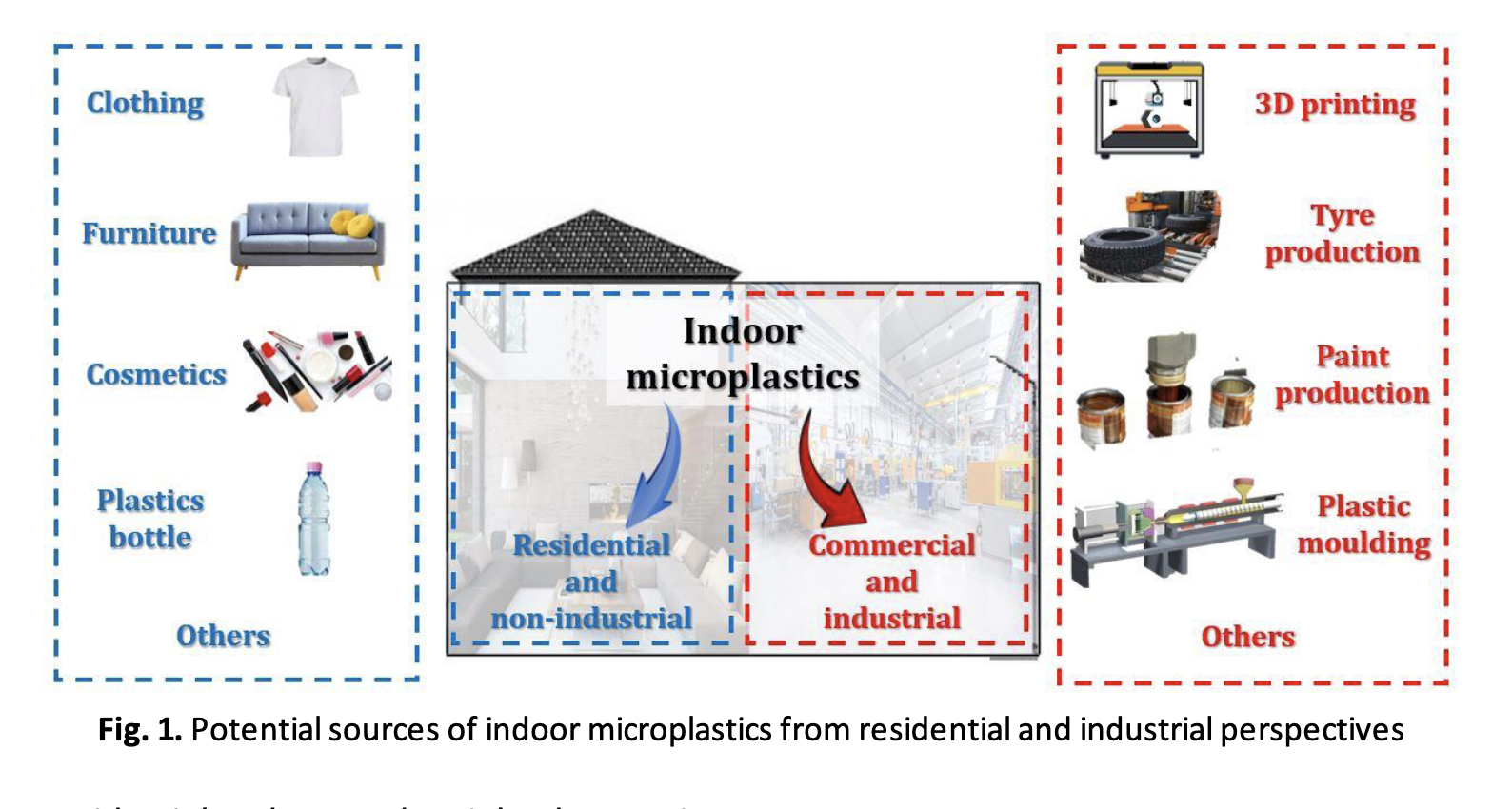
Indoor microplastics present a noteworthy and all-encompassing environmental issue that requires careful attention and contemplation. This comprehensive review navigates the intricate landscape of indoor microplastics, investigating their potential sources, pathways of exposure, and implications for human health. Commencing with an exploration of the origins and varieties of polymers within indoor environments, the review dissects commonplace products and manufacturing processes, identifying them as substantial contributors. Subsequent sections elucidate the diverse ways individuals encounter indoor microplastics, encompassing airborne dissemination, ingestion via dust and food, and skin contact with subsequent absorption. The critical evaluation of advancements in detection and measurement techniques addresses the complexities associated with accurately quantifying indoor microplastics. The review scrutinizes potential health risks linked to exposure, emphasizing cumulative effects and the vulnerability of specific populations. Prolonged contact with heightened concentrations of microplastics can bring about various consequences, including oxidative stress, DNA damage, organ dysfunction, metabolic disorders, immune responses, neurotoxicity, and reproductive and developmental toxicity. In the mitigation segment, strategies are outlined to curb microplastic presence at its source, manage indoor air quality, and advocate for policy and regulatory interventions. Identifying future directions and research gaps, the review serves as a roadmap for ongoing investigations. In summary, this study consolidates crucial discoveries, offers suggestions for future research initiatives, and emphasizes the critical need to understand and tackle the intricate network of indoor microplastics to safeguard both human health and environmental well-being.