A Comparative Study on Various ANN Optimization Algorithms for Magnetorheological Elastomer Carbonyl Iron Particle Concentration Estimation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.16.1.124133Keywords:
Magnetorheological elastomer, carbonyl iron particle, artificial neural network, Adam optimizer, machine learningAbstract
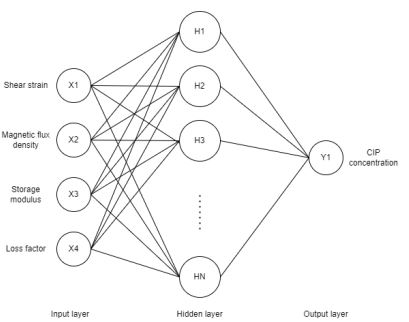
Estimation particle composition such as particle shape, size, and concentration are crucial prior to the fabrication process of magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) to avoid process repetition due to inaccurate formulation. Currently, most of MRE prediction model were purposely used to predict the rheological properties such as shear stress and dynamic modulus, known as forward model. Nonetheless, very few studies have been reported to be capable able of predicting particle composition particularly in MR materials, which known as inverse model. Therefore, this paper proposed a carbonyl iron particle (CIP) concentration based MRE prediction model using neural network algorithm. Neural network-based machine learning model is more approachable compared to conventional mathematical modelling approach due to easily identify trends and pattern while handling multi-variety data. Various optimization algorithms have been employed such as Adam, RMSprop, SGD, AdaGrad, and Nadam throughout the modelling process. As the results, given shear strain amplitude, magnetic flux density, storage modulus, and loss factor as model input, SGD gave the maximum prediction accuracy with 0.95 and 3.038 MPa of R2 and RMSE, respectively. Hence, this model can be the basis to the MRE material and devices development particularly as the tool to reduce costing and time consuming.