Enhancing Energy and Exergy Efficiency in Hot Air Drying System using IoT-Controlled Adaptive Air Recirculation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arefmht.21.1.165181Keywords:
Drying, exergy, IoT control, recycle airAbstract
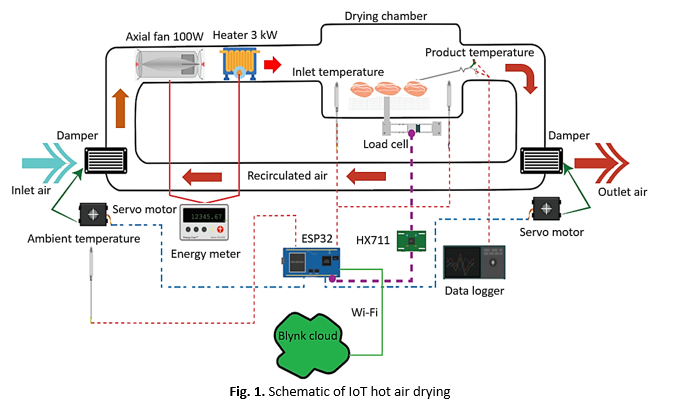
Traditional hot air drying systems consume substantial energy, often accounting for up to 60% of industrial operational costs, presenting significant challenges for sustainable manufacturing processes. Current drying systems rely on static air recirculation settings that cannot adapt to real-time changes in moisture content, leading to inefficient energy utilization and poor energy quality optimization. This study develops an Internet of Things (IoT)-controlled hot air drying system featuring adaptive air recirculation to enhance both energy and exergy efficiency through dynamic real-time control. We investigated the effects of varying air recirculation rates (0%, 25%, 50%, and 75%) across three temperature settings (50°C, 60°C, and 70°C) on specific energy consumption (SEC) and exergy efficiency using fresh pork slices as experimental material with IoT-enabled servo motor control for adaptive recirculation adjustment. The findings indicate that higher temperatures combined with increased air recirculation substantially reduce SEC, achieving reductions of up to 50% under optimal conditions (70°C and 75% recirculation). Furthermore, exergy efficiency improved by up to 42.1%, reflecting a significant decrease in exergy destruction. This IoT-enabled adaptive system demonstrates a robust strategy for minimizing energy consumption and optimizing energy quality in drying processes, providing critical insights for sustainable and high-efficiency drying applications.
Downloads