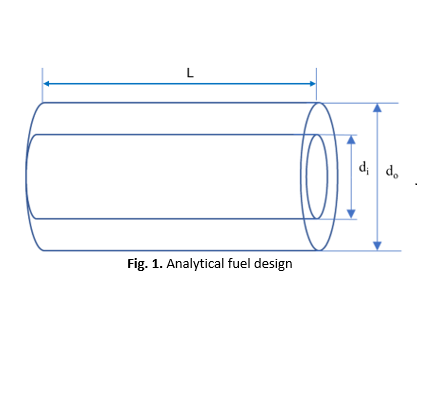
Investigation of Regression Rate Enhancement of HTPB/Paraffin Fuel in the Hybrid Rocket Motor Utilizing High Entropy Alloys Energetic Additives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arefmht.21.1.2337Keywords:
Hybrid rocket motors, high entropy alloy (HEA), regression rate, hybrid rocket fuelAbstract
Hybrid rocket motors are being looked at by the aerospace industry as an alternative to solid and liquid rocket power systems that is safer to use, move and handle. HRM still has several weaknesses that need to be explored such as low regression rate, poor combustion efficiency and also the ability to operate in large sizes. This research aims to conduct performance analytical and experimental comparison of HTPB/Paraffin fuel doped with HEA energetic additives for thrust, specific impulse and regression rates. The research analysed the Hybrid Rocker Motor's performance using ProPeP to determine the specific impulse and characteristic velocity of various propellant mixtures for comparison. Twenty-one HTPB/Paraffin fuel samples, with varying concentrations of energetic additives HEA and Ammonium Perchlorate, were fired on a lab-scale static bench equipped with a feeding system, combustion chamber, nozzle and data acquisition system for measurement and analysis. Analysed the results and determine the regression rate improvement of HTPB/Paraffin fuel with HEA additives and the correlation between regression rate and oxidizer mass flux. The experiment's findings indicated that adding HEA, Ammonium Perchlorate and Aluminium increased the regression rate. HEA demonstrates a 79% improvement, markedly lower than the 128% boost found with AP. Nonetheless, HEA enhances the thermal stability of the fuel mixture. ensuring uniform performance across different oxidizing conditions, as demonstrated in the hybrid formulation containing ammonium perchlorate (AP) and HEA. The integration of AP and HEA enhances heat distribution, hence promoting combustion stability.
Downloads