Estimation of Outlet Water Temperature of a Cooling Tower Based on Weather Data in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arefmht.18.1.4754Keywords:
Cooling tower, Kuala Lumpur weather data, relative humidityAbstract
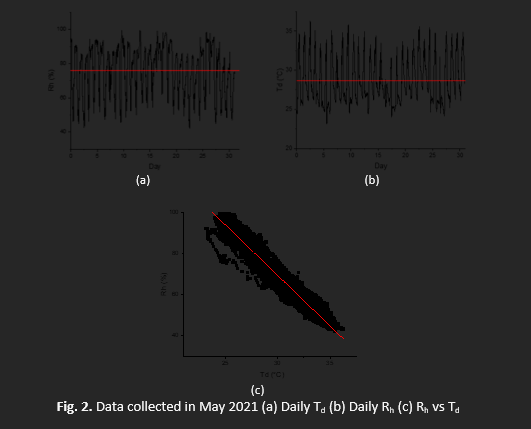
The study centres on predicting the outlet water temperature of a cooling tower in Kuala Lumpur (KL) by evaluating weather data, with the goal of reducing energy usage through improved forecasting. The objective of the study is to develop an accurate prediction equation for obtaining the wet-bulb temperature (Tw) using the dry-bulb temperature (Td) and relative humidity (Rh). This study also aims to prove the coefficient of performance (COP) of refrigeration cycles that are cooled by water from cooling towers. Using a weather station equipped in the UTM-KL campus, the Td and Rh were measured for every minute. The Tw was calculated by applying the bisection method and Sprung's formula to obtain the prediction equation for Tw. The maximum prediction error of the proposed equation for Tw was 0.15 °C. The prediction error by the previously proposed Stull’s formula was 0.69 °C. The COP of the water Carnot cooling refrigeration cycle was 1.9 times higher than that of the air cooling refrigeration cycle.
Downloads