Performance Analysis of a Dual-Generation of Energy Using Hybrid Wind-Solar System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arefmht.18.1.113Keywords:
Hybrid renewable energy system, wind turbine, photovoltaic panel, power generationAbstract
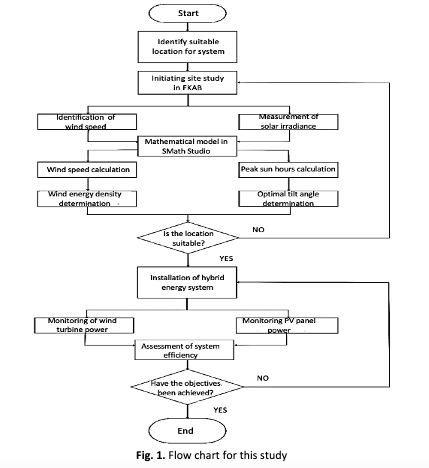
The demand for renewable energy technologies has surged due to the global energy transition and the push for decarbonization. This study explores the development of a Hybrid Renewable Energy System (HRES) combining solar and wind energy, focusing on selecting an optimal location in Malaysia based on available resources and analyzing its power generation and efficiency. A site study using anemometers and pyranometers was conducted from 8 am to 5 pm over five days, and SMath Studio was employed for mathematical modeling to determine average wind speed at varying heights, wind energy density, peak sun hours, and the optimal photovoltaic (PV) panel angle. The HRES, consisting of a Savonius turbine blade and a thin-film PV panel, was installed atop the Fakulti Kejuruteraan Alam Bina academic building. The wind turbine achieved an average power output of 0.2129 W, producing 5.11 Wh/day, while the PV panel generated 6.9083 W, yielding 43.45 Wh/day. Combined, the HRES produced 48.56 Wh/day with an efficiency of 7.02%. The findings demonstrate the suitability of the Savonius turbine for low wind speeds and the effectiveness of solar panels under high irradiance conditions. Although the system's overall efficiency was low, it successfully stabilized power output, determined optimal resource utilization, and provided valuable insights into hybrid energy generation. This study offers practical guidelines for developing dual renewable energy systems and advancing sustainable energy solutions.
Downloads